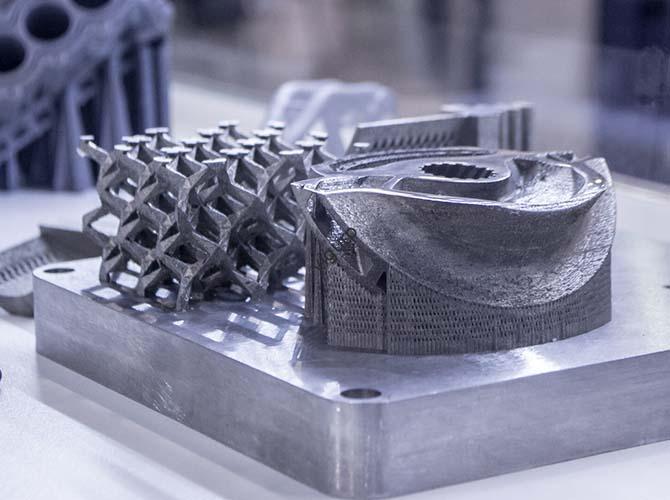
Real-World Examples of 3D Printing Applications: Transforming Industries
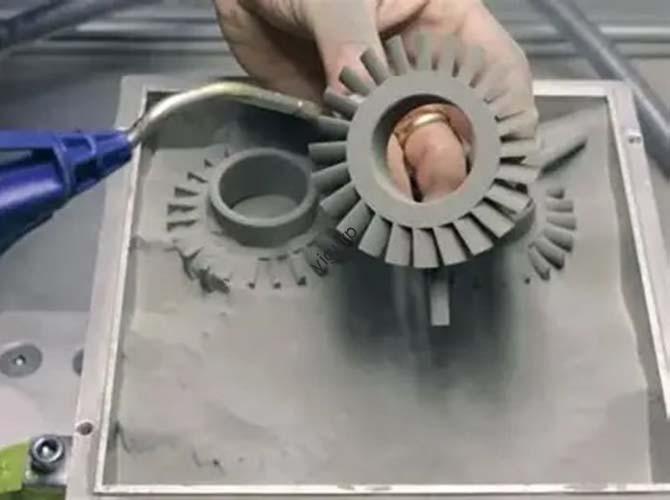
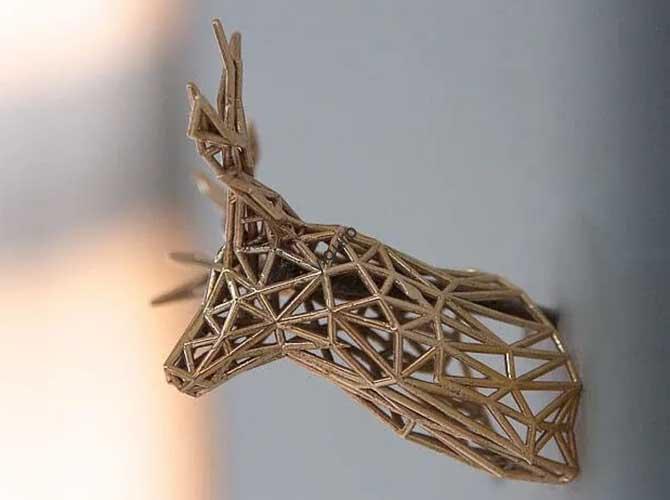
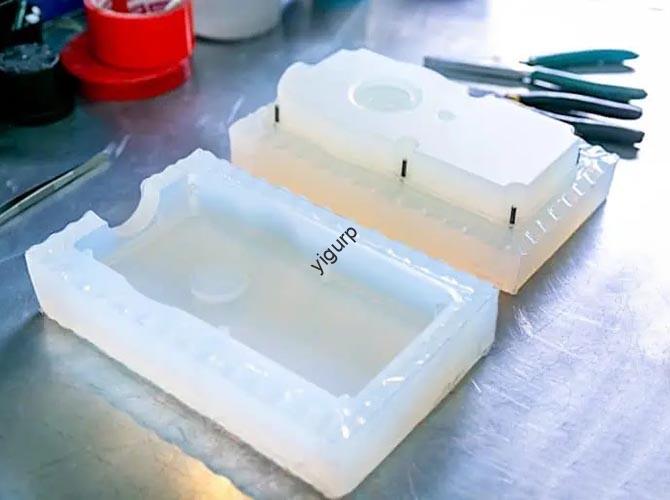
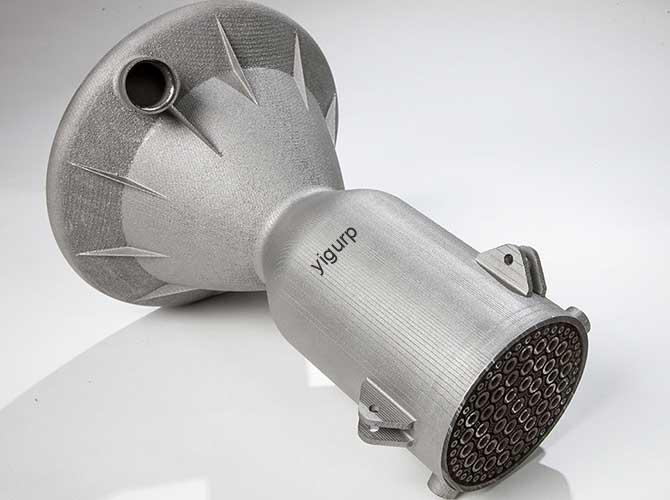
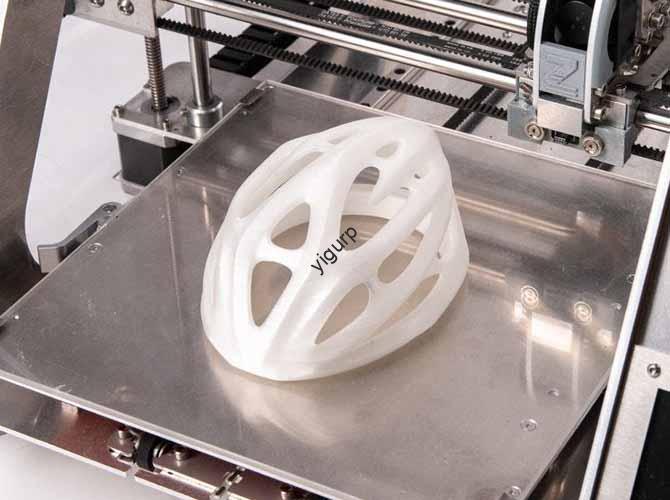
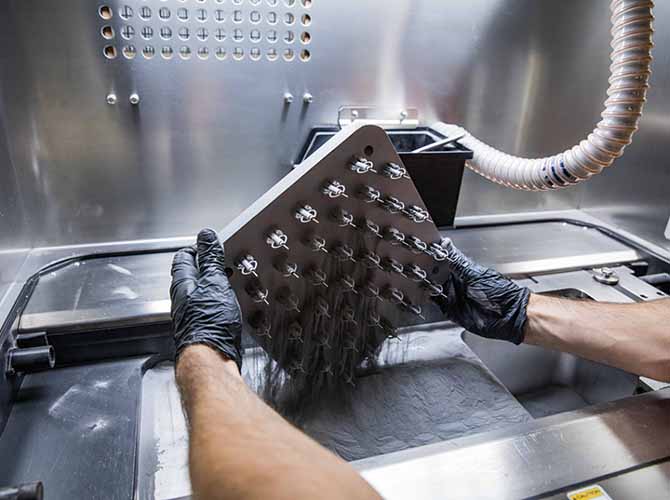
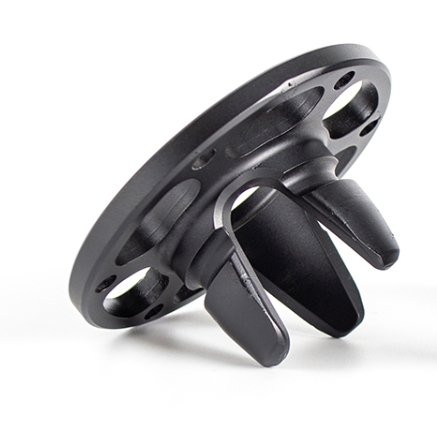
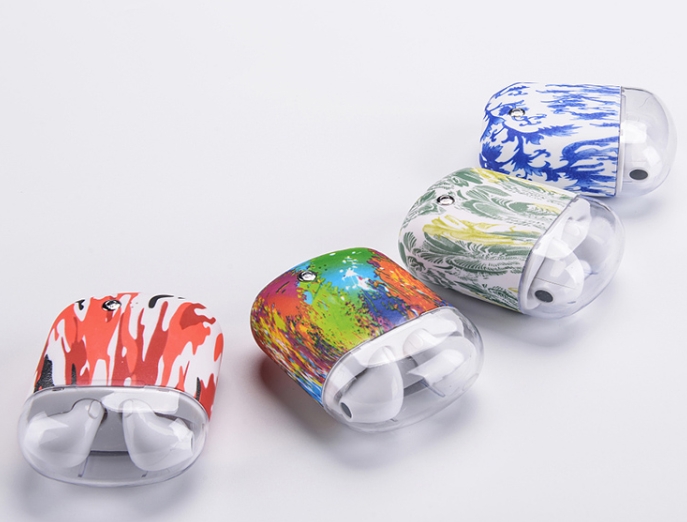
3D printing, once a niche prototyping tool, has evolved into a transformative technology across sectors. But what does it look like in practice? From saving lives in hospitals to revolutionizing how cars are built, examples of 3D printing applications reveal its power to solve real-world problems—whether that’s cutting costs, accelerating innovation, or creating products that were once […]