How Can 3D Printing Achieve Texture Effects, and Which Method to Choose?
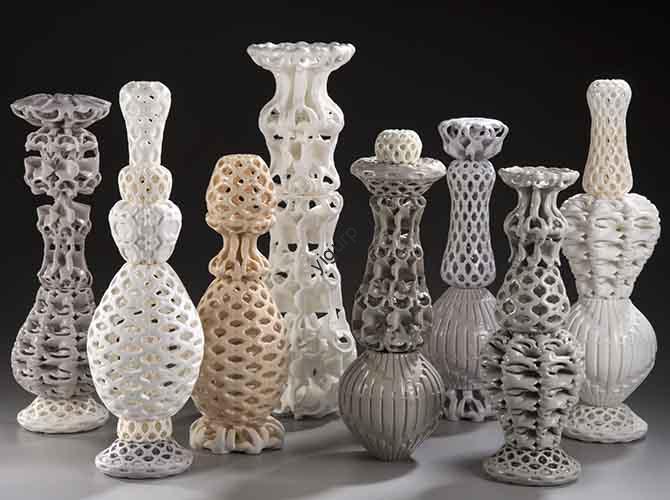
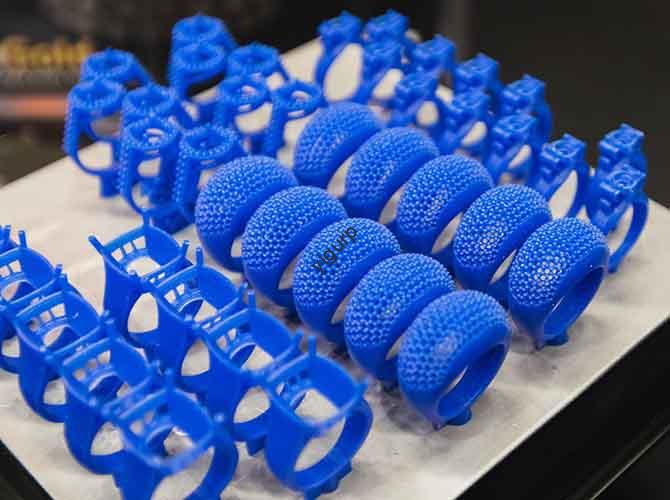
Texture effects—from subtle grain to intricate patterns—elevate 3D printed parts from functional to visually and tactilely engaging. Whether you’re making consumer goods (e.g., textured phone cases), industrial components (e.g., grip-enhanced tool handles), or artistic pieces (e.g., mimicking wood grain), 3D printing offers flexible, scalable ways to add texture. This article answers “How can 3D printing […]