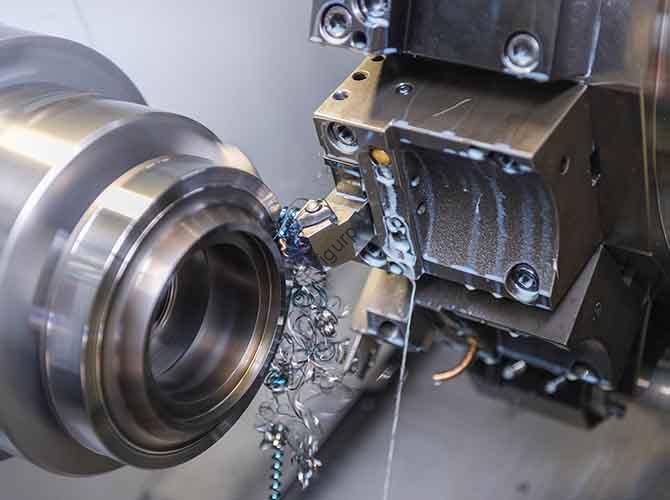
In industrial production, why do automotive and aerospace industries rely on КПН -поворот for cylindrical parts like engine shafts or fuel nozzles? The answer lies in the CNC turning machining process—a computer-controlled method that transforms raw metal bars into high-precision, uniform components with minimal human error. В отличие от ручного точения, which depends on operator skill, CNC turning ensures consistent quality across high-volume runs while handling complex geometries. В этой статье разбивается 6 core stages of the process, ключевые параметры, выбор инструмента, Контроль качества, и реальные приложения, helping you master every step for efficient, accurate part production.
What Is the CNC Turning Machining Process?
CNC Turning Machining Process is an additive-subtractive manufacturing method that uses Computer Numerical Control (Сжигание) systems to rotate a workpiece while a cutting tool shapes it into cylindrical or conical forms. The process removes excess material from the workpiece (typically metal bars, 5–100mm in diameter) to create features like outer circles, end faces, канавки, нить, или конус.
Think of it as a “digital lathe operator”: it follows pre-programmed G-code and M-code to control tool movement, Скорость шпинделя, and feed rate—executing repetitive tasks with micron-level accuracy (up to ±0.01mm) и 24/7 последовательность. It’s ideal for producing rotational parts, from small electronic connectors to large industrial shafts.
6 Core Stages of the CNC Turning Machining Process
Процесс протекает линейно, error-proof workflow—each stage builds on the last to ensure part quality. Ниже приведена подробная разбивка каждого шага, with actionable tips and common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Анализ процесса (Фонд успеха)
Process analysis is the first and most critical step—it defines how the part will be machined. Key tasks include:
- Part Drawing Interpretation: Extract critical details from 2D/3D drawings:
- Dimensional requirements (НАПРИМЕР., Внешний диаметр: 20± 0,02 мм, длина: 100мм).
- Surface finish standards (НАПРИМЕР., Раствор < 1.6μm for visible areas).
- Material type (НАПРИМЕР., алюминиевый сплав 6061, нержавеющая сталь 304).
- Machining Content Selection: Decide which features to machine (НАПРИМЕР., отверстия, нить, канавки) and their order—follow the “from rough to fine” principle (roughing removes 80–90% of excess material first; finishing refines precision).
- Sequence Optimization: Avoid repositioning the workpiece unnecessarily. Например:
- Machine the outer circle → 2. Drill the center hole → 3. Cut threads → 4. Finish the end face.
Pitfall to Avoid: Skipping process analysis leads to tool collisions or out-of-tolerance parts. Например, machining threads before drilling a center hole can cause the workpiece to vibrate, ruining thread accuracy.
2. Выбор инструмента (Match Tools to Material & Функции)
The right tool directly impacts machining efficiency and surface quality. Use this table to select tools based on material and feature type:
| Тип инструмента | Идеальные материалы | Key Features Machined | Советы по оборудованию |
| External Turning Tools | Все металлы (алюминий, сталь, титан) | Outer circles, конус, end faces | – Используйте карбидные вставки (НАПРИМЕР., CCMT 09T304) for high-speed machining (150–200 m/min for aluminum). – HSS Инструменты (НАПРИМЕР., W18Cr4V) for low-speed, high-precision finishing. |
| Drilling Tools | Мягкие металлы (алюминий, медь); low-hardness steel (45#) | Through holes, Слепые отверстия | – Twist drills for small holes (≤10mm); indexable drills for large holes (>10мм). – Use coolant to reduce heat buildup (prevents drill bit wear). |
| Threading Tools | Сталь (304, 45#), алюминиевые сплавы | External threads (НАПРИМЕР., M10×1.5), internal threads | – Indexable threading inserts (НАПРИМЕР., 16IR 1.5 Iso) for fast thread cutting. – Single-point threading tools for non-standard thread pitches. |
| Grooving Tools | Все металлы; best for ductile materials (алюминий, латунь) | External grooves (НАПРИМЕР., snap ring grooves), internal grooves | – Use narrow-blade tools (ширина: 0.5–5 мм) to avoid material buildup. – Уменьшите скорость подачи (0.05–0.1mm/rev) for deep grooves (prevents tool breakage). |
Пример: Machining M8×1.25 threads on a stainless steel 304 shaft → Choose a 16IR 1.25 ISO threading insert with TiAlN coating (resists wear from stainless steel’s high hardness).
3. Настройка параметров резки (Balance Speed, Кормить, & Глубина)
Параметры резки (скорость, скорость корма, глубина разрезания) determine how fast and accurately the part is machined. Below are optimized parameters for common materials:
| Материал | Скорость резки (Vc, м/мой) | Скорость корма (фон, мм/rev) | Глубина разрезания (доступа, мм) | Key Reasoning |
| Алюминиевый сплав 6061 | 150–200 | 0.15–0,3 | Грубая: 2–5; Отделка: 0.1–0,5 | Aluminum’s low hardness (HB 60–90) allows high speeds; avoid excessive depth (causes deformation). |
| Нержавеющая сталь 304 | 80–120 | 0.1–0,2 | Грубая: 1–3; Отделка: 0.1–0,3 | Высокая твердость (HB 150–180) requires slower speeds; use coolant to reduce heat (prevents work hardening). |
| Углеродистая сталь 45# | 120–180 | 0.12–0.25 | Грубая: 1.5–4; Отделка: 0.1–0.4 | Balances speed and tool life; carbide tools work best for high-speed roughing. |
Formula Tip: Calculate spindle speed (Не, об/мин) using N = (1000 × Vc) / (π × D), where D = workpiece diameter (мм). Например, a 20mm aluminum shaft at Vc=180 m/min → N = (1000×180)/(3.14×20) ≈ 2866 об/мин.
4. Программирование с ЧПУ (Translate Design to Machine Code)
Programming converts process analysis results into code the CNC machine understands. Key codes and a sample program for a simple shaft are shown below:
| Code Type | Common Codes & Functions |
| G-код (Motion Control) | – G00: Rapid positioning (no cutting). – G01: Linear interpolation (cutting at constant feed). – G71: Rough turning cycle. – G70: Finishing cycle. – G76: Thread cutting cycle. |
| M-Code (Machine Functions) | – M03: Spindle on (clockwise rotation). – M08: Охлаждающая жидкость на. – M30: Program end (reset to start). |
Sample Program for a 20mm×100mm Aluminum Shaft:
O0001 (Program Number)G21 G99 G97 (Metric units, feed per rev, constant speed)T0101 (Tool 01: External turning; Offset 01)M03 S2800 (Spindle on CW, 2800 rpm)M08 (Coolant on)G00 X25 Z2 (Rapid to start position)G71 U2 R1 (Roughing cycle: depth 2mm, retract 1mm)G71 P10 Q20 U0.2 W0.1 F0.2 (Finish allowance: X0.2mm, Z0.1mm; feed 0.2mm/rev)N10 G00 X18 Z2 (Start of roughing contour)G01 X20 Z0 F0.15 (Cut to Z0)Z-100 (Cut to length 100mm)N20 G01 X25 Z-100 (End of roughing contour)G70 P10 Q20 (Finishing cycle)G00 X100 Z100 (Rapid to safe position)M05 (Spindle off)M09 (Coolant off)M30 (Program end)Ключевой совет: Use simulation software (НАПРИМЕР., Мастеркам, Слияние 360) to test programs before physical machining—this avoids tool collisions and overcuts.
5. Заготовка заготовки & Позиционирование (Обеспечить стабильность)
Proper clamping prevents workpiece vibration (a major cause of poor surface finish). Следуйте этим рекомендациям:
- Chuck Selection:
- Three-jaw chucks for round workpieces (self-centering, Быстрая настройка).
- Four-jaw chucks for irregular shapes (adjustable jaws for precise centering).
- Tailstock Support: For long workpieces (length > 5× diameter), use a tailstock center to reduce bending. Например, a 100mm-long, 20mm-diameter shaft needs tailstock support to avoid vibration during roughing.
- Runout Check: Use a dial indicator to measure radial runout (should be < 0.01мм). Excess runout (НАПРИМЕР., 0.05мм) causes uneven cutting, leading to out-of-tolerance diameters.
6. Test Cut Inspection & Parameter Adjustment (Validate Before Mass Production)
Never skip test cuts—they let you correct errors before wasting materials. Процесс включает в себя:
- Test Cut Execution: Machine 1–2 sample parts using the programmed parameters.
- Проверка размерных:
- Use calipers for outer diameters/lengths (accuracy ±0.02mm).
- Use a micrometer for precise measurements (НАПРИМЕР., нить шаг, groove width—accuracy ±0.001mm).
- Use a surface roughness tester to check Ra values (ensure they meet drawing requirements).
- Parameter Adjustment:
- If surface finish is rough (Ra > 3.2μm): Уменьшите скорость подачи на 20% or increase cutting speed.
- If diameter is too small (НАПРИМЕР., 19.98mm instead of 20mm): Increase the X-axis offset by 0.02mm.
Пример: A test cut aluminum shaft has a diameter of 19.95mm (цель: 20± 0,02 мм). Adjust the X-offset by +0.05mm—subsequent parts will meet the target dimension.
Реальный случай: Machining Aluminum Alloy 6061 Валы
- Проблема: An automotive supplier needs 10,000 aluminum shafts (20mm×100mm) с:
- Внешний диаметр: 20± 0,02 мм.
- Поверхностная отделка: Раствор < 1.6мкм.
- Время производства: < 2 минуты на часть.
- CNC Solution:
- Анализ процесса: Грубая (ap=3mm) → Drilling (center hole, φ3mm) → Finishing (ap=0.2mm) → Deburring.
- Инструменты: T01 (CCMT 09T304 carbide insert), T02 (φ3mm twist drill).
- Параметры: Vc=180 m/min, f=0.2mm/rev, N=2866 rpm.
- Program: Use G71 roughing + G70 finishing cycles (reduces program length by 50%).
- Результат:
- Точность размеров: 99.8% of parts meet 20±0.02mm.
- Время производства: 1.8 минуты на часть (meets target).
- Жизнь инструмента: Carbide inserts last 500 части (reduces tool change time by 80%).
Перспектива Yigu Technology
В Yigu Technology, Мы видим CNC turning machining process as the backbone of precision cylindrical part production. Our CNC lathes (YG-T200) are optimized for this process: they have high-speed spindles (до 6,000 об/мин) for aluminum machining, smart tool offset systems (auto-corrects dimensional errors by ±0.005mm), and integrated coolant recycling (reduces waste by 30%). We’ve helped automotive clients cut production time by 35% and aerospace firms achieve ±0.008mm accuracy for critical parts. As Industry 4.0 advances, we’re adding AI-driven parameter optimization—our software now auto-suggests cutting speeds/feeds based on material, reducing operator skill requirements and ensuring consistent quality.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
- Q.: What’s the difference between rough turning and finish turning in the CNC turning process?
А: Rough turning removes most excess material (80–90%) at high feed rates (0.15–0.3mm/rev) and large depths of cut (2–5 мм)—prioritizes speed over surface finish. Finish turning uses small depths (0.1–0,5 мм) and slow feeds (0.05–0.15mm/rev)—prioritizes precision (± 0,01 мм) и гладкие поверхности (Раствор < 1.6мкм).
- Q.: How to avoid tool breakage during CNC turning of hard materials like stainless steel?
А: Use these tips: 1) Choose TiAlN-coated carbide tools (сопротивляться износу); 2) Уменьшить глубину разреза (1–3mm for roughing); 3) Increase coolant flow (cools tool and workpiece); 4) Avoid interrupted cuts (НАПРИМЕР., machining grooves in hard spots).
- Q.: Can CNC turning machine non-metallic materials like plastic or wood?
А: Да! Для пластмасс (НАПРИМЕР., Пома, АБС), Используйте высокоскоростную сталь (HSS) инструменты (prevents melting) and low cutting speeds (50–80 m/min). For wood, use specialized woodturning tools (НАПРИМЕР., carbide-tipped scrapers) and high feeds (0.3–0.5mm/rev)—CNC turning produces smooth wooden parts like handles or decorative spindles.