When it comes to manufacturing screws—critical components in everything from electronics to aerospace—how do you ensure every piece meets strict size, thread, and strength standards? The answer lies in the CNC machining screw process—a computer-controlled workflow that turns raw metal into high-precision fasteners with unmatched consistency. Это руководство разрушает весь процесс, solves common pain points, and helps you understand why CNC is the top choice for screw production.
1. What Is the CNC Machining Screw Process?
А CNC machining screw process использует компьютерное числовое управление (Сжигание) technology to automate the cutting, формирование, and threading of screws. В отличие от ручной обработки (which relies on human skill to operate tools), CNC systems follow preprogrammed instructions to produce screws with tight tolerances—often as small as ±0.001 inches.
Think of it like baking cookies with a precise recipe: the CNC program is your “recipe,” and the machine is your oven—consistently turning out perfect results every time. For screws, this consistency is non-negotiable: a poorly sized screw can ruin an electronic device or compromise a building’s structure.
2. The 8-Step CNC Machining Screw Process (Linear Workflow)
Creating a screw via CNC machining follows a clear, repeatable sequence. Skip a step, and you risk defects—so let’s walk through each stage in order:
- Design Modeling with CAD Software: Первый, использовать Атмосфера (Компьютерный дизайн) инструменты (НАПРИМЕР., Солидворкс, Autocad) to build a 3D model of the screw. This model includes every detail: нить шаг (НАПРИМЕР., 2мм), head shape (плоский, pan, or hex), и длина (НАПРИМЕР., 10мм). Without an accurate CAD model, the final screw won’t fit its intended use.
- Data Conversion to Machine-Readable Format: Export the CAD model to an STL or STEP file—formats CNC machines can “understand.” This step bridges the gap between design and manufacturing: if the file is corrupted, the machine will misinterpret the design.
- Programming with CAM Software: Использовать Камера (Компьютерное производство) software to turn the 3D model into G-code—the language of CNC machines. The G-code tells the machine exactly how to move: tool speed (НАПРИМЕР., 1,500 Rpm), cutting depth, and thread spacing. Например, a G-code line might say, “Cut a 2mm thread for 10mm along the metal rod.”
- Raw Material Selection & Подготовка: Choose the right material based on the screw’s use. Общие варианты включают:
- Нержавеющая сталь: Для коррозионной стойкости (НАПРИМЕР., outdoor furniture screws).
- Углеродистая сталь: Для силы (НАПРИМЕР., construction screws).
- Сплава Сталь: Для приложений с высокими нагрузками (НАПРИМЕР., automotive engine screws).
Cut the raw material into rods of the correct length (НАПРИМЕР., 12mm for a 10mm screw, leaving extra for machining).
- Зажим & Позиционирование: Secure the metal rod in the CNC machine’s chuck (a clamping device) and align it precisely. Even a 0.005-inch misalignment can make the screw’s thread uneven—so operators use laser sensors to ensure perfect positioning.
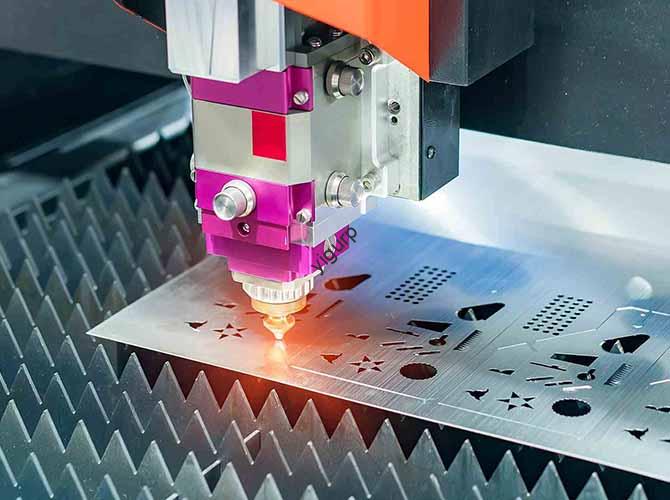
- Обработка с ЧПУ (Резка, Threading, Формирование): The machine executes the G-code, using tools like drills (для отверстий) and taps (for threading) to shape the screw. This stage may include:
- Поворот: Spinning the rod while a tool cuts the head shape.
- Фрезерование: Carving grooves or slots (НАПРИМЕР., a Phillips head).
- Threading: Using a tap to cut spiral threads into the rod.
A single CNC machine can produce 500+ screws per hour—10x faster than manual machining.
- Качественная проверка: Test every batch of screws for key metrics:
- Точность размеров (НАПРИМЕР., is the diameter exactly 5mm?).
- Thread accuracy (НАПРИМЕР., does it fit a standard nut?).
- Качество поверхности (no burrs or scratches).
Inspectors use calipers and thread gauges—if even 1% of screws fail, the batch is reworked.
- После лечения & Отделка: Improve the screw’s durability with post-processing:
- Выслушивание: Removing sharp edges (prevents hand injuries during installation).
- Термическая обработка: Heating and cooling to strengthen the metal (НАПРИМЕР., for high-stress screws).
- Покрытие: Adding a layer of zinc or chrome for corrosion resistance (НАПРИМЕР., bathroom screws).
- Packing & Warehousing: Package 合格 screws in boxes (НАПРИМЕР., 100 screws per box) and store them in a dry warehouse to avoid rust. Ready for shipment to manufacturers or retailers.
3. Обработка с ЧПУ против. Traditional Manual Machining for Screws
Why choose CNC over manual machining for screw production? Let’s compare the two methods with hard data:
| Фактор | CNC Machining Screw Process | Традиционная ручная обработка |
| Точность | Tolerances of ±0.001–±0.005 inches | Tolerances of ±0.01–±0.05 inches (Зависит от навыка оператора) |
| Скорость производства | 500–1,000 screws per hour | 50–100 screws per hour |
| Последовательность | 99.9% of screws meet standards | 80–90% consistency (varies by operator) |
| Labor Cost | 1 operator monitors 3–5 machines | 1 operator per machine |
| Лучше всего для | High-volume runs (1,000+ винты) or precision parts | Маленькие партии (100–500 screws) or simple designs |
4. 3 Common Problems in CNC Machining Screw Process (И как их исправить)
Even with CNC’s precision, Вопросы могут возникнуть. Here are the top pain points and solutions:
| Проблема | Причина | Решение |
| Uneven Threads | Misaligned raw material or dull threading tool | Use laser alignment tools and replace taps every 5,000 винты. |
| Screw Head Cracks | Too much pressure during turning or low-quality material | Reduce tool pressure by 10% and use certified alloy steel (НАПРИМЕР., ASTM A325). |
| Rust After Production | Humidity during post-treatment or poor plating | Dry screws in a 60°C oven for 30 minutes and use a 2-layer zinc plating. |
5. Yigu Technology’s Perspective on CNC Machining Screw Process
В Yigu Technology, Мы оптимизировали CNC machining screw process для 100+ clients—from electronics makers to aerospace companies. The biggest issue we solve? Custom screw production. Many clients need non-standard screws (НАПРИМЕР., a 3mm thread with a custom hex head), and our CAD/CAM team can turn their design into a production-ready program in 24 часы.
We also use AI-powered inspection tools to cut defect rates to 0.5%—half the industry average. Например, a medical device client now produces 10,000 precision screws monthly with our process, meeting FDA standards with zero rejections. As CNC tech advances, we’ll keep making the process faster and more affordable for small-batch orders.
Часто задаваемые вопросы: Your Top CNC Machining Screw Process Questions Answered
1 квартал: How long does it take to set up the CNC machining screw process for a new screw design?
А1: For a standard design (НАПРИМЕР., a 5mm pan-head screw), setup takes 4–6 hours (CAD modeling + G-code programming). Для пользовательских дизайнов (НАПРИМЕР., unique thread patterns), it may take 1–2 days—but this is still 5x faster than manual machining setup.
2 квартал: Can the CNC machining screw process handle small batch orders (НАПРИМЕР., 50 винты)?
А2: Да! CNC’s low setup cost makes it ideal for small batches. В отличие от инъекционного литья (который требует дорогих форм), CNC can switch between designs in hours—so 50 screws cost only slightly more per unit than 5,000.
Q3: What’s the most durable material for CNC-machined screws?
А3: Это зависит от использования. For outdoor or wet environments, нержавеющая сталь 316 лучше (сопротивляется коррозии соленой воды). Для приложений с высокими нагрузками (НАПРИМЕР., двигатели), Сплава Сталь 4140 (тепло) offers the highest strength—can withstand up to 120,000 psi of pressure.