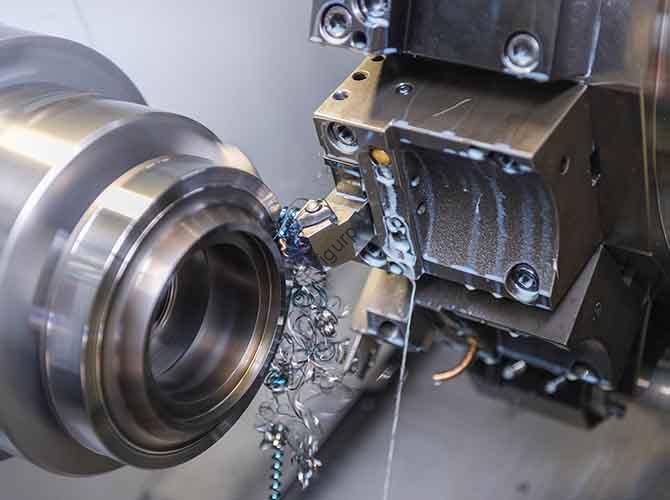
Se você atua na indústria automotiva, seja você um fabricante, engenheiro, ou comprador - você provavelmente já ouviu o termo “CNC automotivo” espalhado por aí. Mas o que é exatamente, e por que isso é importante para a construção de carros? Simplificando, CNC automotivo (Controle Numérico Computadorizado) refere-se a máquinas controladas por computador que cortam, forma, furar, ou fresar materiais como metal, plástico, and composites for automotive parts. Ao contrário da usinagem manual, CNC uses pre-programmed software to ensure every part is identical, preciso, and consistent—critical for an industry where even a 0.1mm error can ruin a safety component like a brake caliper.
Resumidamente, automotive CNC isn’t just a “tool”—it’s the backbone of modern auto manufacturing. It’s why today’s cars are safer, isqueiro, and more reliable than ever, and it’s a non-negotiable for any brand looking to scale production or meet strict industry standards. Let’s break down everything you need to know, from how it works to how to choose the right system for your needs.
Key Applications of Automotive CNC in Car Production
Automotive CNC isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution—it’s used across nearly every stage of building a car, from small engine components to large body frames. Abaixo estão os mais comuns (e crítico) aplicações, with real-world examples to show how they impact production.
Engine and Transmission Components
The engine is the “heart” of a car, and its parts need ultra-tight tolerances to avoid leaks, superaquecimento, ou fracasso. CNC machines excel here: they produce parts like virabrequins, árvores de cames, e engrenagens de transmissão with precision down to 0.001mm. Por exemplo, Toyota uses CNC turning centers to machine crankshafts for its hybrid engines. Before CNC, a skilled machinist might take 2 hours to make one crankshaft, with slight variations between parts. Agora, a CNC machine can produce 10 identical crankshafts per hour—cutting labor time by 80% and reducing defect rates from 5% to less than 0.1%, according to Toyota’s 2024 Manufacturing Report.
Chassis and Safety Parts
The chassis (the car’s “frame”) and safety components (like brake rotors and suspension brackets) need to be strong and consistent to protect drivers. CNC milling machines are often used here, as they can shape thick metal sheets into complex, load-bearing structures. Take BMW’s chassis production for the 3 Series: their CNC gantry mills cut aluminum alloy into chassis rails that are 30% mais leve que o aço, mas igualmente forte. This weight reduction helps improve fuel efficiency by 12% (per BMW’s 2023 Sustainability Report) while meeting global crash safety standards.
Interior and Exterior Trim
Even cosmetic parts benefit from automotive CNC. For interior components like dashboard panels or door handles, CNC routers cut plastic or composite materials into precise shapes that fit perfectly with other parts. Externally, CNC machines shape parts like hoods and fenders—ensuring every car off the line has the same sleek look. Ford, por exemplo, uses CNC routers to cut the interior panels of its F-150 trucks. This eliminates the “gap issues” common with manual cutting, where panels might not line up, leading to customer complaints. Ford reports a 40% drop in interior fitment issues since switching to CNC for this process.
Why Automotive CNC Is Non-Negotiable for Modern Auto Makers
Você pode estar se perguntando: Can’t auto manufacturers just stick with manual machining or older technologies? The short answer is no—not if they want to compete. Below are the core benefits that make automotive CNC essential, backed by data and industry insights.
Unmatched Precision and Consistency
Manual machining relies on human skill, which means even the best machinist will make small errors. CNC eliminates this: once the program is set, cada parte é idêntica. Para peças automotivas, this consistency is critical. Por exemplo, a brake pad that’s 0.5mm too thick won’t fit, and a bolt that’s slightly off-thread could cause a part to loosen. According to the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), parts made with CNC have a tolerance accuracy 10x higher than those made manually. This reduces defect rates from an average of 3-4% (manual) para 0.05-0.1% (CNC)—saving manufacturers millions in rework and recalls.
Faster Production Speeds
Auto manufacturing is all about scale—brands like Volkswagen or Hyundai produce thousands of cars per day. Máquinas CNC funcionam 24/7 without fatigue, cutting production time for key parts by 50-70%. Por exemplo, machining a transmission gear manually might take 90 minutos; a CNC lathe can do it in 25 minutos. The International Federation of Robotics (IFR) reports that auto plants using CNC machines have a production output 3x higher than those relying on manual labor. This speed is crucial for meeting consumer demand and staying ahead of competitors.
Flexibility for Design Innovation
Modern cars are getting more complex—think electric vehicles (VEs) with unique battery housings or self-driving cars with sensor mounts. CNC machines can adapt to these new designs quickly: just update the software, and the machine can start making the new part. Manual machining, por contraste, would require new tools and retraining workers, which takes weeks or months. Tesla is a great example: when they redesigned the battery pack for the Model Y, they updated their CNC programs in 24 hours and were producing the new battery housings the next day. Without CNC, this transition would have taken 6-8 semanas, delaying the Model Y’s launch by months.
Cost Savings Over Time
Embora as máquinas CNC tenham um custo inicial mais alto (tipicamente \(50,000-\)500,000, depending on the type), they save money long-term. Here’s how:
- Less labor: One operator can run 3-4 Máquinas CNC, contra. one machinist per manual machine.
- Menos defeitos: As mentioned, lower defect rates mean less rework and no costly recalls.
- Maior vida útil da ferramenta: CNC machines use tools more efficiently, reducing tool replacement costs by 20-30%.
UM 2024 study by McKinsey found that auto manufacturers who invest in CNC technology see a return on investment (ROI) dentro de 18-24 meses—a timeline that’s hard to beat with other manufacturing upgrades.
Types of CNC Machines Used in Automotive Manufacturing
Not all CNC machines are the same—different tasks require different tools. Below is a breakdown of the most common types used in auto production, along with their uses and examples.
| Tipo de máquina | Primary Use in Automotive | Vantagem Principal | Example Part Produced |
| Torno CNC | Turning cylindrical parts (por exemplo, eixos, parafusos) | Rápido, precise for round shapes | Crankshaft, wheel hub |
| CNC Milling Machine | Cutting flat or complex 3D shapes (por exemplo, colchetes, blocos de motor) | Can handle thick materials | Suspension bracket, engine block |
| CNC Router | Cutting soft materials (por exemplo, plástico, madeira, compósitos) | Ideal for interior/exterior trim | Dashboard panel, door handle |
| CNC Plasma Cutter | Cutting thick metal sheets (por exemplo, chassis parts, body panels) | Fast for large, flat metal parts | Chassis rail, truck bed |
| 5-Axis CNC Machine | Complexo, multi-angle parts (por exemplo, Carcaças de bateria EV, exhaust manifolds) | Can reach all sides of a part without repositioning | EV battery housing, exhaust manifold |
Real-World Example: Tesla uses 5-axis CNC machines to produce the battery housings for the Model 3. These housings need to be both lightweight and strong enough to protect the battery, and they have complex grooves for cooling. A 5-axis machine can cut all these features in one go, whereas a standard 3-axis machine would require repositioning the part 3-4 times—adding time and increasing the risk of errors. Tesla says this process cuts battery housing production time by 40%.
How to Choose the Right Automotive CNC System for Your Needs
Investing in CNC is a big decision—you need to pick a system that fits your production volume, part type, e orçamento. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you choose, with questions to ask yourself along the way.
Etapa 1: Define Your Core Needs
Start by answering these questions:
- What parts will you make? If you’re making cylindrical parts (like bolts), a CNC lathe is best. If you’re making complex 3D parts (like engine blocks), a 5-axis mill is better.
- What’s your production volume? Para pequenos lotes (100-500 partes/mês), a entry-level CNC machine (\(50,000-\)100,000) funciona. For high volume (10,000+ partes/mês), you’ll need industrial-grade machines (\(200,000-\)500,000) with automation features.
- What materials will you use? Metal (alumínio, aço) requires more powerful machines than plastic or composites. Por exemplo, cutting steel needs a CNC mill with a high-torque spindle, while cutting plastic can use a lower-power router.
Etapa 2: Evaluate Key Features
Once you know your needs, look for these features in a CNC system:
- Faixa de tolerância: For safety parts (por exemplo, componentes de freio), aim for ±0.001mm. For cosmetic parts (por exemplo, aparar), ±0.05mm is acceptable.
- Software Compatibility: Ensure the machine works with your existing CAD/CAM software (por exemplo, AutoCAD, SolidWorks). Some machines come with proprietary software—make sure it’s easy to use and update.
- Automation Options: For high volume, look for machines with robotic loaders (to feed materials automatically) or integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) for real-time production tracking.
- After-Sales Support: CNC machines need regular maintenance. Choose a supplier that offers 24/7 apoiar, spare parts, and training for your team.
Etapa 3: Compare Suppliers and Get References
Don’t just pick the first supplier you find. Ask for:
- Estudos de caso: Do they have experience working with automotive clients? Por exemplo, have they supplied machines to brands like Ford or GM?
- References: Talk to other auto manufacturers who use their machines. Ask about uptime (how often the machine breaks down) and support response time.
- Warranty: A good warranty should cover parts and labor for 1-2 anos. Some suppliers offer extended warranties for an extra cost—worth considering for high-use machines.
Exemplo: A small auto parts supplier making 500 suspension brackets per month would likely choose a 3-axis CNC mill (\(80,000-\)120,000) with basic automation. A large OEM like Toyota, fazendo 10,000 crankshafts per month, would invest in a line of CNC lathes ($200,000 each) with robotic loaders and MES integration.
Common Challenges with Automotive CNC (and How to Solve Them)
While automotive CNC is powerful, it’s not without challenges. Below are the most common issues manufacturers face, along with practical solutions.
Desafio 1: High Upfront Cost
Many small to mid-sized manufacturers struggle with the initial investment. Solução: Look for financing options (por exemplo, leases or loans) from suppliers or third-party lenders. Some suppliers offer “used but refurbished” CNC machines that are 30-40% cheaper than new ones, with warranties. Por exemplo, Haas Automation offers a lease program where monthly payments start at \(1,500 for a basic CNC lathe—far more manageable than a \)50,000 upfront cost.
Desafio 2: Skilled Labor Shortages
CNC machines require operators who can program and maintain them, but there’s a shortage of skilled CNC technicians in the auto industry. Solução: Partner with local technical schools to create training programs. Por exemplo, Ford partners with community colleges in Michigan to offer CNC technician courses—students get hands-on training and a job at Ford after graduation. You can also invest in user-friendly software (por exemplo, Fanuc’s Quick Set) that simplifies programming, so less-experienced operators can still run the machines.
Desafio 3: Machine Downtime
Even the best CNC machines break down, and downtime costs auto manufacturers \(2,000-\)5,000 per hour (per the Manufacturing Technology Insights 2024 Relatório). Solução: Implement a preventive maintenance schedule. Por exemplo, clean the spindle every week, replace filters every month, and have a technician do a full inspection every 6 meses. Também, keep spare parts (por exemplo, ferramentas de corte, sensores) in stock so you can fix issues quickly. Some suppliers offer “predictive maintenance” tools that use sensors to alert you when a part is about to fail—reducing unexpected downtime by 50%.
Yigu Technology’s Perspective on Automotive CNC
Na tecnologia Yigu, we believe automotive CNC is the cornerstone of next-gen auto manufacturing—especially as the industry shifts to electric and autonomous vehicles. EVs need lightweight, peças de alta precisão (como caixas de bateria e componentes de motor) that only CNC can produce consistently. Our team has worked with auto suppliers to integrate smart CNC solutions, like AI-powered programming software that cuts setup time by 30% and predictive maintenance tools that boost machine uptime to 95%. We also see a trend toward “connected CNC”—machines that share data with other systems (por exemplo, inventory management, controle de qualidade) to create a seamless production line. Para fabricantes, investing in CNC isn’t just about today’s needs—it’s about preparing for a future where speed, precisão, and flexibility will define success.
FAQ About Automotive CNC
1. How much does an automotive CNC machine cost?
Costs vary by type and capability: Entry-level CNC lathes or routers start at \(50,000-\)100,000. Industrial-grade 5-axis mills or plasma cutters cost \(200,000-\)500,000. Refurbished machines are 30-40% mais barato, and leases can lower monthly costs to \(1,500-\)5,000.
2. Can CNC machines make parts for electric vehicles (VEs)?
Absolutely—EVs rely heavily on CNC. CNC machines produce battery housings (lightweight and leak-proof), motor shafts (alta precisão), and charging port components (consistent fit). Many EV manufacturers (like Tesla and BYD) use 5-axis CNC machines for these parts.
3. How long does it take to train a worker to operate an automotive CNC machine?
Basic operation (loading materials, starting programs) takes 1-2 weeks with user-friendly software. Advanced skills (programação, manutenção) take 3-6 months of training. Partnering with technical schools or using supplier training programs can speed this up.
4. What’s the difference between 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machines for automotive use?
3-axis machines move in three directions (X, S, Z) and are good for simple parts (por exemplo, colchetes). 5-axis machines add two more rotational axes, so they can cut complex parts (por exemplo, Carcaças de bateria EV) from all angles without repositioning—saving time and reducing errors.
5. How do I maintain an automotive CNC machine to avoid downtime?
Follow a preventive maintenance schedule: Clean components weekly, replace filters monthly, and do full inspections every 6 meses. Keep spare parts in stock, and consider predictive maintenance tools that alert you to potential issues. This can reduce downtime by 50% ou mais.