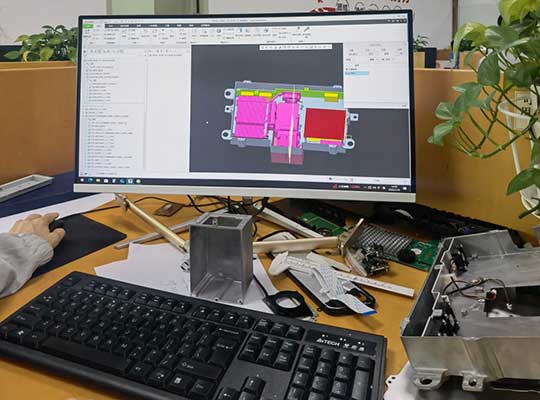
When it comes to CNC metal prototype (also known as CNC metal prototype) pemesinan, achieving high surface quality and precision is crucial. One key post-processing step that directly affects the final product’s performance and appearance is deburring. Burrs—those small, unwanted metal projections formed during cutting, penggerudian, or milling—can cause assembly issues, damage tools, and even pose safety risks. Dalam panduan ini, we’ll break down the most effective deburring methods for CNC metal prototypes, help you choose the right one for your project, and share tips to minimize burrs from the start.
1. Common Deburring Methods for CNC Metal Prototypes
Not all deburring methods work for every prototype. The choice depends on factors like part complexity, bahan, saiz batch, and precision requirements. Below is a detailed breakdown of the most widely used techniques, along with their pros, cons, and ideal use cases.
| Deburring Method | Prinsip Kerja Teras | Kes penggunaan yang ideal | Kecekapan (1-10) | Ketepatan (1-10) | Tahap kos |
| Manual Deburring | Menggunakan alat tangan (fail, kertas pasir, scrapers) to grind away burrs | Prototaip berbentuk kompleks, Kumpulan kecil (1-10 bahagian) | 3 | 7 | Rendah |
| Punch Press Deburring | Using a custom mold with a punch press to shear off burrs | Simple flat-surface prototypes, Kumpulan sederhana (10-50 bahagian) | 7 | 6 | Medium (mold cost included) |
| Grinding Deburring (Vibration, Sandblasting, Tumbling) | Using abrasive materials (Mis., ceramic beads, pasir) to rub against parts and remove burrs | Large batches (50+ bahagian), parts with multiple small burrs | 8 | 5 | Medium |
| Mechanical Deburring | Using automated tools (brushes, grinding wheels, deburring robots) to remove burrs | Pengeluaran volum tinggi (100+ bahagian), standard-shaped prototypes | 9 | 8 | Sederhana tinggi |
| Chemical Deburring | Immersing parts in a chemical solution to dissolve burrs via chemical reaction | Prototypes made of specific metals (Mis., aluminium, Tembaga), parts with hard-to-reach burrs | 6 | 7 | Medium (chemical cost) |
| Electrochemical Deburring | Using an electric current to electrolyze and dissolve burrs (works with conductive metals) | Prototaip ketepatan (Mis., perubatan, aerospace parts) | 5 | 10 | Tinggi |
| Heat Treatment Deburring | Heating the prototype to soften or break off burrs (Mis., low-temperature annealing) | Prototypes with heat-resistant materials (Mis., aloi keluli) | 4 | 4 | Rendah-medium |
| Laser Deburring | Using a high-precision laser beam to vaporize burrs without touching the part | Ultra-high-precision prototypes (toleransi < 0.001mm) | 6 | 10 | Tinggi |
| Ultrasonic Deburring | Menggunakan gelombang bunyi frekuensi tinggi (20-40khz) to agitate a liquid and abrasive mixture, which removes burrs | Kecil, delicate prototypes (Mis., micro-components) | 7 | 9 | Medium |
2. Key Factors to Choose the Right Deburring Method
Selecting the best deburring technique isn’t random. You need to consider 4 critical factors to balance quality, kos, and efficiency:
- Bahan prototaip: Different metals react differently to deburring. Contohnya, aluminium is soft and works well with chemical or ultrasonic deburring, manakala Keluli tahan karat (harder material) may require laser or mechanical deburring.
- Kerumitan bahagian: Intricate prototypes with internal holes or narrow slots (Mis., aerospace components) are hard to reach with manual tools—opt for ultrasonik atau electrochemical deburring sebaliknya.
- Production Batch: If you’re making 1-5 prototaip, manual deburring adalah kos efektif. Untuk 50+ bahagian, grinding deburring (vibration/tumbling) atau automated mechanical deburring will save time.
- Precision Requirements: Medical prototypes or high-end electronics often need tolerances under 0.005mm—laser atau electrochemical deburring is the only way to avoid damaging the part while removing burrs.
3. How to Minimize Burrs During CNC Machining (Reduce Post-Processing Work)
The best way to handle burrs is to prevent them from forming in the first place. By optimizing your CNC machining process, you can cut down deburring time by 30-50%. Inilah 3 practical tips:
- Choose Burr-Minimizing Cutting Tools: Use sharp, high-quality tools (Mis., carbide end mills for steel) and avoid worn-out blades—dull tools tend to push metal instead of cutting it, creating larger burrs.
- Optimize Machining Parameters: Adjust the cutting speed, feed rate, dan depth of cut. Contohnya, increasing the feed rate slightly (within safe limits) can reduce burr formation on aluminum prototypes.
- Design for Deburring: When drafting the prototype’s 3D model, avoid sharp internal corners (use a minimum radius of 0.1mm) and leave extra space around hard-to-reach areas. This makes post-processing easier, even for manual deburring.
4. Yigu Technology’s Perspective on CNC Metal Prototype Deburring
Di Yigu Technology, we believe deburring is not just a “fix” but a critical part of delivering high-quality CNC metal prototypes. Our team combines method selection dengan process optimization: Untuk batch kecil, complex prototypes, we use manual deburring with precision files to ensure no detail is missed; for high-volume, standard parts, we rely on automated mechanical deburring to boost efficiency. We also prioritize pre-machining planning—by adjusting cutting parameters and tool choices, we’ve helped clients reduce deburring costs by up to 40%. The goal is always to balance speed, kos, and precision to meet each client’s unique needs.
FAQ About CNC Metal Prototype Deburring
Q1: Can I skip deburring for my CNC metal prototype?
Tidak. Even small burrs can cause problems: they may scratch mating parts during assembly, interfere with measurements (affecting precision), or pose safety risks (Mis., sharp edges can cut hands). Deburring ensures the prototype functions as intended and meets quality standards.
S2: Which deburring method is the cheapest for small-batch prototypes?
Manual deburring is the most cost-effective for small batches (1-10 bahagian). It requires no expensive equipment—only basic hand tools like files and sandpaper. Walau bagaimanapun, it’s labor-intensive, so it’s not ideal for large batches.
Q3: Is laser deburring suitable for all metal materials?
Tidak. Laser deburring works best with metals that absorb laser energy well, such as steel, Titanium, and aluminum. It’s less effective for highly reflective metals (Mis., copper or gold), as the laser may bounce off the surface instead of vaporizing burrs. For reflective metals, electrochemical deburring is a better choice.