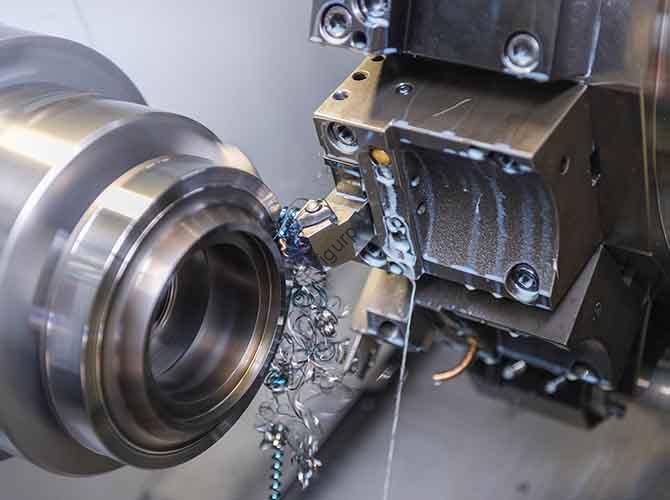
CNC machining accuracy—defined by how closely a finished part matches its design specifications—is the backbone of high-quality manufacturing. Ha un impatto diretto sulla funzionalità della parte, adattamento dell'assemblaggio, e durabilità a lungo termine, sia che produciate componenti aerospaziali o dispositivi medici. Questo articolo analizza il typical accuracy ranges of CNC machining across equipment types, fattori chiave che influenzano, and practical strategies to achieve target precision, aiutandoti a prendere decisioni informate per i tuoi progetti.
1. CNC Machining Accuracy Ranges by Equipment Type
Different CNC machines—from ordinary lathes to ultra-precision grinders—deliver vastly different accuracy levels. Below is a detailed table of achievable dimensional accuracy (tolleranza) e rugosità superficiale (Ra), tailored to match equipment to your project’s needs.
| CNC Equipment Type | Sub-Equipment | Precisione dimensionale (Tolleranza) | Rugosità superficiale (Ra) | Typical Application Scenarios |
| Tornio CNC | Ordinary CNC Lathe | IT7–IT8 (±0.01–0.02 mm) | 1.6–10 µm | General-purpose parts (per esempio., low-speed shafts, non-critical housings) |
| High-Precision CNC Lathe | ±0.005 mm or better | 0.04–0.8 μm | Precision rotating parts (per esempio., alberi di trasmissione automobilistici) | |
| Mirror Turning Lathe (Metalli non ferrosi) | ±0.001–0.003 mm | 0.01–0.04 μm | Alta brillantezza, ultra-precision parts (per esempio., optical instrument components, aluminum decorative parts) | |
| CNC Milling Machine/Machining Center | Ordinary Milling Machine | IT7–IT8 (±0.01–0.02 mm) | 1.6–6.3 μm | Parti strutturali (per esempio., telai di macchine, bracket blanks) |
| Ultra-High Precision Milling Machine | ±0,001 mm | 0.4–0.08 μm | Nuclei dello stampo, aerospace structural components | |
| Five-Axis Machining Center | ±0,01 mm | 0.63–1.6 μm | Complex surface parts (per esempio., pale della turbina, automotive engine cylinder heads) | |
| Rettificatrice CNC | Cylindrical Grinder | ±0,001 mm | 0.04–0.4 μm | Parti soggette ad alta usura (per esempio., gare dei cuscinetti, pezzi di utensili) |
| Surface Grinder | ±0,002 mm | 0.08–0.32 μm | Flat precision parts (per esempio., mold bases, machine tool guideways) | |
| Elettroerosione a filo | Fast Wire EDM | ±0,02 mm | 6.3 µm | Low-precision metal cutting (per esempio., prototype blanks, non-critical templates) |
| Slow Wire EDM | ±0,002 mm | 0.2 µm | High-precision die/mold parts (per esempio., stamping die cavities, ingranaggi di precisione) |
2. Key Factors That Influence CNC Machining Accuracy
Achieving target accuracy isn’t just about choosing the right machine—it depends on controlling four critical variables. Below is a breakdown of each factor and its real-world impact:
2.1 Machine Tool Performance
The machine’s built-in capabilities lay the foundation for accuracy:
- Rigidità: A rigid machine frame reduces vibration during cutting. Per esempio, a low-rigidity milling machine may flex under heavy cutting loads, leading to ±0.03 mm errors—double the target tolerance.
- Risoluzione: High-precision machines use grating scales (con 0.1 μm resolution) to track tool movement, while ordinary machines rely on ball screws (1–5 μm resolution), limiting their accuracy.
- Stabilità termica: Temperature fluctuations cause metal parts to expand or contract. Machines with thermostatic control systems (maintaining 20°C ±1°C) reduce thermal errors by 70% compared to unregulated machines.
2.2 Tool Quality & Indossare
Tools directly shape the part—poor tool condition destroys accuracy:
- Materiale dello strumento: Diamond tools (for non-ferrous metals) maintain sharp edges longer, enabling mirror turning (Ra 0.01 µm). Utensili in metallo duro (per acciaio) wear faster, requiring replacement every 2–3 hours to avoid Ra 0.8 μm → 1.6 μm degradation.
- Wear Management: A dull tool leaves uneven cuts. Per esempio, a worn end mill may produce a slot with ±0.02 mm width error, instead of the target ±0.01 mm.
2.3 Parametri di lavorazione
Optimizing cutting speed, velocità di avanzamento, and depth of cut is critical:
- Velocità di taglio: Too low = tool rubbing (rough surface); too high = thermal deformation. Per alluminio, 300–500 m/min speed balances accuracy and efficiency.
- Tasso di avanzamento: Smaller feed rates (per esempio., 0.1 mm/rev vs. 0.3 mm/giro) reduce tool marks, lowering Ra from 1.6 μm a 0.8 µm.
2.4 Environmental Control
Workshop conditions often get overlooked but matter greatly:
- Temperature: Aluminum alloy parts expand by 0.01 mm per meter for every 1°C temperature rise. A constant-temperature workshop (20°C ±1°C) eliminates this error.
- Vibration: Nearby heavy machinery (per esempio., preme) causes vibration, leading to wavy surfaces. Vibration isolation foundations reduce such errors by 80%.
3. Practical Accuracy Selection: Match Tolerance to Application
Not all parts need ultra-high accuracy—over-specifying wastes time and money. Below is a guide to standard tolerance grades (per ISO 2768) and their cost implications:
| Tolerance Grade | ISO 2768 Specifica (0.5–3mm Size) | Applicazioni tipiche | Impatto sui costi (contro. Medium Grade) |
| Precisione (F) | ±0,05 mm | Parti aerospaziali, impianti medici (per esempio., artificial joints) | +50% costo (requires ultra-precision machines) |
| Medio (M) | ±0,1 mm | Componenti di motori automobilistici, general machinery | Base cost (0% increase) |
| Ruvido (C) | ±0,2 mm | Staffe strutturali, low-precision assemblies | -30% costo (uses ordinary machines) |
Esempio: Automotive Part Accuracy Selection
- Engine Cylinder Bore: Needs Precision Grade (±0,05 mm) to ensure piston fit—poor accuracy causes oil leaks.
- Chassis Bracket: Uses Medium Grade (±0,1 mm) — looser tolerance doesn’t affect structural performance.
- Plastic Cover Clip: Uses Rough Grade (±0,2 mm) — cost savings outweigh minor size variations.
4. Yigu Technology’s Perspective on CNC Machining Accuracy
Alla tecnologia Yigu, we often see clients chase “higher accuracy than needed”—for example, specifying ±0.005 mm for a non-critical bracket that only requires ±0.1 mm, aumentando i costi di 80%. Il nostro consiglio: Start with the part’s functional requirements, not the machine’s maximum capability. For most industrial projects, Medium Grade (±0,1 mm) balances performance and cost. When ultra-precision is needed (per esempio., parti aerospaziali), we combine slow wire EDM (±0,002 mm) with online laser inspection to validate accuracy in real time. We also optimize processes for clients—recently, adjusting a milling machine’s thermal control reduced a client’s aluminum part errors from ±0.02 mm to ±0.01 mm, without new equipment. This “needs-first, optimization-focused” approach ensures clients get accurate parts at the right cost.
Domande frequenti: Common Questions About CNC Machining Accuracy
- Q: Can a five-axis machining center achieve the same accuracy as a ultra-high precision milling machine?
UN: NO. Five-axis machines excel at complex surfaces but have a typical accuracy of ±0.01 mm, while ultra-high precision milling machines reach ±0.001 mm. For simple, parti di alta precisione (per esempio., nuclei dello stampo), the latter is better.
- Q: How much does environmental control affect accuracy for small parts (per esempio., 10mm size)?
UN: Significant. A 1°C temperature change causes a 10mm aluminum part to expand by 0.000023 mm (negligible), but for a 1m part, suo 0.023 mm (critical). Per piccole parti, vibrazione (not temperature) is the bigger risk—even minor vibration can cause ±0.005 mm errors.
- Q: If my part needs ±0.001 mm accuracy, which CNC process should I choose?
UN: Ultra-precision grinding or mirror turning (for non-ferrous metals) are the only options. Slow wire EDM reaches ±0.002 mm, which is insufficient. You’ll also need a constant-temperature workshop, utensili diamantati, and online inspection to maintain this accuracy.