3Stampa D, O produzione additiva, si è evoluto da uno strumento di prototipazione di nicchia a una soluzione versatile per settori che vanno dall'aerospaziale alla gioielleria. Ma con così tante tecnologie a disposizione, come si fa a scegliere quello giusto?? The key lies in understanding the methods of 3D printing—each with unique principles, punti di forza, e casi d'uso ideali. Whether you’re a hobbyist making desk models, a manufacturer producing metal parts, or a designer crafting intricate jewelry, this guide breaks down the six most common 3D printing methods to help you solve your specific challenges.
1. SLA (Stampaggio fotopolimerizzabile): Precision for Intricate Designs
SLA, short for Light Curing Molding, is a resin-based 3D printing method that excels at creating highly detailed, smooth-surface parts.
Come funziona
SLA uses a laser beam to cure liquid photosensitive resin layer by layer, following a CAD (Progettazione assistita da computer) file. The resin hardens when exposed to the laser, building the part from the bottom up. A platform lowers slightly after each layer, allowing the next layer of resin to be cured—like drawing with light in liquid.
Pro & Contro
| Vantaggi | Disadvantages |
| Altissima precisione (0.02–0.1mm layer height) | High equipment cost (\(5,000–)100,000+) |
| Liscio, almost finished surfaces (no post-sanding needed for many uses) | Limited material options (mostly photosensitive resins) |
| Ideal for complex geometries (per esempio., jewelry details, modelli dentali) | Resin may be toxic (requires gloves and ventilation) |
Real-World Use Case
A jewelry designer needed to create a custom ring with tiny floral engravings. Using SLA, they printed a resin prototype in 4 hours—with every petal and leaf detail intact. The prototype was then used to make a mold for metal casting, saving weeks of hand-carving time. For anyone needing fine details and smooth finishes, SLA is the go-to method.
2. SLS (Sinterizzazione laser selettiva): Versatility Across Materials
SLS, or Selective Laser Sintering, stands out for its ability to print with a wide range of materials—from plastics to ceramics—making it a favorite for industrial applications.
Come funziona
SLS uses a high-powered laser to “sinter” (heat and fuse) powdered materials layer by layer. Unlike SLA, it doesn’t need liquid resin; instead, it spreads a thin layer of powder (per esempio., nylon, metallo) across a build platform. The laser fuses the powder in the shape of the part’s cross-section, and unsintered powder remains to support the part—no extra support structures needed.
Pro & Contro
| Vantaggi | Disadvantages |
| Supports diverse materials (plastica, metalli, ceramica) | High operating cost (powder is pricey; \(50–)200/kg) |
| No need for support structures (unsintered powder acts as support) | Post-processing is cumbersome (removing powder, levigatura) |
| Creates strong, parti durevoli (good for functional prototypes) | Equipment is expensive (\(10,000–)500,000+) |
Real-World Use Case
An automotive manufacturer needed to test a new gear design for a hybrid car. Using SLS with nylon powder, they printed 10 gear prototypes in 24 ore. The parts were strong enough to withstand test runs, and since no supports were needed, the team avoided time-consuming post-processing. Per multi-material, parti funzionali, SLS delivers.
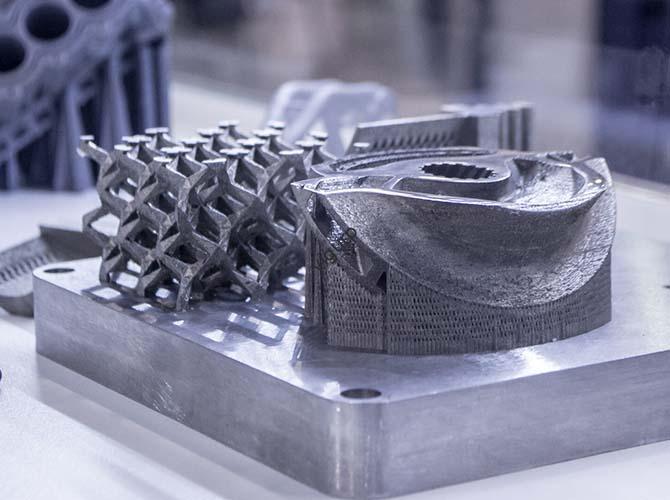
3. SLM (Fusione laser selettiva): High-Strength Metal Parts
SLM, or Selective Laser Melting, is often confused with SLS—but it’s designed specifically for metals, creating fully dense, high-strength parts for demanding industries.
Come funziona
SLM uses a laser to melt polvere metallica (per esempio., titanio, acciaio inossidabile) completely, rather than just sintering it. This full melting results in parts with the same strength as traditionally manufactured metal components. Like SLS, it uses unsintered powder for support, but the process requires tighter temperature control to avoid warping.
Pro & Contro
| Vantaggi | Disadvantages |
| Produces fully dense metal parts (99–100% density) | Extremely high cost (attrezzatura: \(100,000–)1M+) |
| Ideal for aerospace/automotive (withstands high pressure/temperatures) | Needs professional operators (complex temperature control) |
| Can make complex metal geometries (per esempio., pale della turbina, impianti medici) | Slow print speed (metal melting takes time) |
Real-World Use Case
Aerospace engineers needed a lightweight, strong bracket for a jet engine. Using SLM with titanium powder, they printed a bracket that was 30% lighter than the traditional aluminum version—without losing strength. The bracket’s complex internal channels (for cooling) would have been impossible to make with CNC machining. Per high-performance metal parts, SLM is unmatched.
4. LOM (Layered Solid Manufacturing): Low-Cost Prototyping
LOM, or Layered Solid Manufacturing, is a budget-friendly method that uses sheet materials (like paper or plastic film) to create simple prototypes.
Come funziona
LOM cuts sheet materials into the shape of the part’s cross-section using a laser or blade. Each cut layer is glued to the one below it, building up the 3D part. The excess material around the part acts as support, which is removed after printing.
Pro & Contro
| Vantaggi | Disadvantages |
| Basso costo (materiali: paper/plastic film, \(1–)5 per sheet) | Low part strength (glued layers are brittle) |
| Fast print speed (no melting—just cutting/gluing) | Limited detail (can’t make small, intricate parts) |
| Simple operation (no need for advanced training) | Narrow application (only for prototyping, not functional parts) |
Real-World Use Case
A furniture designer wanted to test the shape of a new chair before investing in woodworking. Using LOM with paper sheets, they printed a full-size chair prototype in 8 hours—costing just $20 in materials. The prototype let them adjust the chair’s curves for better ergonomics, without wasting expensive wood. Per cheap, quick design verification, LOM is perfect.
5. FDM (Fused Deposition Manufacturing): Accessible for Everyone
FDM, or Fused Deposition Manufacturing, is the most common 3D printing method—used by hobbyists, schools, and small businesses for its low cost and ease of use.
Come funziona
FDM melts a thermoplastic filament (per esempio., PLA, ABS, PETG) through a heated nozzle, then deposits the melted plastic layer by layer according to a CAD file. The nozzle moves along X/Y axes to draw each layer, and the build platform lowers for the next layer. Supports are needed for overhangs (per esempio., a figure’s outstretched arm).
Pro & Contro
| Vantaggi | Disadvantages |
| Low equipment cost (\(200–)15,000) | Lower precision (0.1–0.3mm layer height) |
| Easy to use (ideal for beginners/hobbyists) | Rough surface (needs sanding for smoothness) |
| Diverse, affordable materials (PLA: \(15–)30/kg) | Slow for large parts (layer-by-layer deposition) |
Real-World Use Case
A high school STEM class wanted to build robot parts for a competition. Using FDM printers with PLA filament, students printed gears, parentesi, and robot arms—each part costing less than $5. The printers were easy to operate, and students could iterate on designs in a day. Per hobbisti, istruzione, or small-scale prototyping, FDM is the most accessible choice.
6. 3DP (3D Printed Molding): Fast Colorful Models
3DP, or 3D Printed Molding (also called binder jetting), is a unique method that creates colorful, low-cost models by bonding powder with adhesive.
Come funziona
3DP uses a nozzle to spray a liquid adhesive onto a layer of powder (per esempio., plaster, ceramica). The adhesive bonds the powder in the shape of the part’s cross-section, e il processo si ripete fino al completamento della parte. It can even print in color by adding pigment to the adhesive.
Pro & Contro
| Vantaggi | Disadvantages |
| Fast print speed (bonds powder quickly) | Low part strength (brittle, not for functional use) |
| Can print in full color (no post-painting needed) | Limited detail (adhesive spread reduces precision) |
| Low material cost (powder: \(10–)30/kg) | Needs sealing (parts absorb moisture easily) |
Real-World Use Case
A toy company wanted to test a colorful action figure design. Using 3DP, they printed a full-color prototype in 6 hours—with the figure’s red cape, blue body, and yellow accessories all printed at once. The prototype let them test consumer reactions to the color scheme without spending on paint. Per veloce, colorful, non-functional models, 3DP is ideal.
How to Choose the Right 3D Printing Method?
With six methods to pick from, the best choice depends on your needs. Use this quick guide:
| Your Goal | Best Method | Key Reason |
| Intricate, parti lisce (jewelry/dental) | SLA | Alta precisione, superfici lisce |
| Multi-material functional parts (industriale) | SLS | Diverse materials, no supports |
| High-strength metal parts (aerospace/medical) | SLM | Fully dense, strong metal |
| Cheap, quick prototypes (design verification) | LOM | Basso costo, velocità veloce |
| Hobby/education/small-scale parts | FDM | Accessible, conveniente |
| Veloce, colorful models (toys/marketing) | 3DP | Full color, fast printing |
La prospettiva della tecnologia Yigu
Alla tecnologia Yigu, we help clients across industries pick the right 3D printing method. For hobbyists/schools, we recommend FDM for its affordability. For industrial clients needing metal parts, SLM or SLS works—we often pair SLS with nylon for functional prototypes to cut costs. For high-end jewelry or dental models, SLA delivers unmatched detail. We also guide clients on post-processing: SLA parts need resin cleaning, while SLS needs powder removal. The key is matching the method to your budget, materiale, and precision needs—3D printing’s power lies in its versatility.
Domande frequenti
- Which 3D printing method is cheapest for beginners?
FDM is the cheapest—entry-level printers cost \(200–)500, and PLA filament is \(15–)30/kg. It’s also easy to learn, making it perfect for beginners.
- Can any 3D printing method make metal parts?
Only SLM and SLS (with metal powder) make metal parts. SLM is better for high-strength, dense parts (per esempio., aerospaziale), while SLS metal parts are less dense (good for non-critical components).
- Which method is best for full-color 3D prints?
3DP (binder jetting) is the only method that prints full color directly. Other methods need post-painting—e.g., FDM or SLA parts can be painted, but it adds time and cost.