Pourquoi les artistes, créateurs, and cultural institutions turning to 3D printing crafts? Contrairement à l'artisanat traditionnel qui repose sur le savoir-faire et le temps., 3L'impression D transforme les idées numériques en art physique avec une flexibilité inégalée, résolvant des problèmes tels qu'une portée de conception limitée., production lente, et difficulté à reproduire des détails complexes. Cet article explique le fonctionnement de l'impression 3D pour l'artisanat, ses principaux avantages, utilisations réelles, and tips to avoid common mistakes, helping you unlock new creative possibilities.
How Does 3D Printing Crafts Work?
À la base, 3D printing crafts follow a 4-step linear process that turns virtual designs into tangible art. Each step is critical—skip one, and you risk flawed results:
- Modélisation numérique: Create a 3D model using software like Tinkercad (beginner-friendly) or Blender (avancé). For cultural heritage projects, use 3D scanners to capture existing relics (par ex., a broken ceramic vase) into digital files.Pour un pourboire: Add fine details (par ex., patterns on a sculpture) in the model—3D printing can reproduce even 0.1mm-wide lines.
- Tranchage: Convert the 3D model into layer-by-layer instructions using slicing software (par ex., Traitement). Set parameters like layer height (0.1–0.2mm for smooth finishes) and infill (10–50% for crafts—higher infill = sturdier pieces).
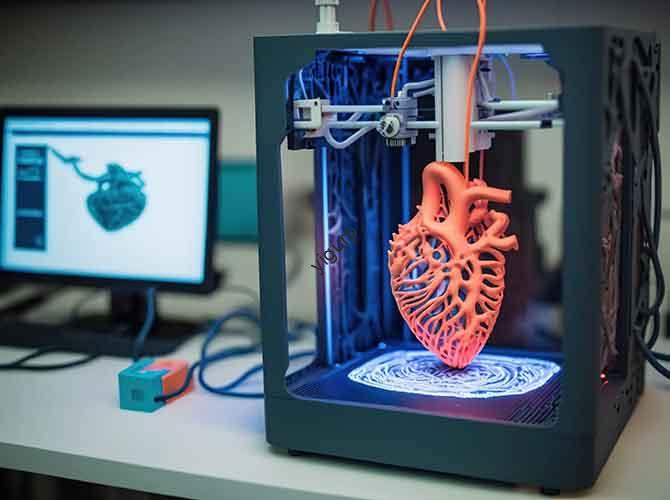
- Impression: Load the sliced file into a 3D printer and select the right material (plastiques, céramique, or biodegradable filaments). The printer deposits material layer by layer—for example, a small decorative lamp takes 4–6 hours to print.
- Post-traitement: Refine the printed piece to enhance its look and feel:
- Sand rough edges with 200–400-grit sandpaper.
- Paint with acrylics or apply varnish for a glossy finish.
- For ceramic crafts, fire the printed piece in a kiln (1200–1300°C) to harden it.
3D Printing Crafts vs. Traditional Handmade Crafts: A Clear Comparison
Many creators wonder: “Is 3D printing better than traditional crafting?” The answer depends on your goals—but 3D printing solves key limitations of manual work. Here’s a side-by-side contrast:
| Aspect | 3D Impression Artisanat | Traditional Handmade Crafts |
|---|---|---|
| Liberté de conception | Can create complex shapes (par ex., hollow sculptures with internal patterns) that are impossible to carve by hand. | Limited by physical tools and human skill—complex details often require years of practice. |
| Vitesse de production | A small souvenir takes 4–8 hours; 10 identical pieces take ~10 hours (with multiple printers). | One small souvenir takes 1–2 days; 10 identical pieces take 10–20 days. |
| Cohérence | Every printed piece is identical (tolérance ±0,1 mm)—ideal for 批量 gifts or exhibitions. | Variations between pieces are common (par ex., slight differences in a hand-painted mug). |
| Options matérielles | Works with plastics (PLA, ABS), céramique, wood-based filaments, and even biodegradable materials. | Relies on traditional materials (argile, bois, métal) that may be hard to source or shape. |
Key Benefits of 3D Printing Crafts (And How They Solve Problems)
3D printing isn’t just a “trend”—it solves real challenges for crafters, artists, and cultural organizations. Voici 4 core benefits with concrete examples:
1. Unmatched Design Flexibility
- Problème: A sculptor wants to create a statue with interlocking parts (no glue needed) but can’t carve the delicate connections by hand.
- Solution: 3D print the statue with pre-designed interlocking joints—each part fits perfectly, and the design would be impossible to replicate manually.
2. Cost-Effective Small-Batch Production
- Problème: A small business wants to make 50 custom wedding favors (par ex., personalized keychains) but can’t afford the time or labor for handmade pieces.
- Solution: 3Impression D 50 keychains in 2 jours (en utilisant 2 imprimantes) at a cost of $2–$3 per piece—vs. $10–$15 per handmade keychain.
3. Cultural Heritage Preservation
- Problème: A museum has a fragile ancient pottery shard that can’t be displayed publicly (risk of breaking) and needs a replica for exhibitions.
- Solution: 3D scan the shard, repair cracks in the digital model, then print an exact replica—visitors can view the replica, and the original is safely stored.
4. Sustainable Crafting
- Problème: A crafter wants to reduce waste (traditional crafting often leaves leftover materials like scrap wood or clay).
- Solution: Use biodegradable PLA filament for 3D printing—leftover material can be melted and reused, and printed pieces decompose in 6–24 months if composted.
Real-World Applications of 3D Printing Crafts
From home decor to cultural preservation, 3D printing crafts are making an impact across industries. Voici 3 inspiring use cases:
- Décoration d'intérieur: A designer in Paris created 3D printed lamp shades with floral patterns that change color when lit. The complex lattice structure (0.5mm d'épaisseur) prendrait 20+ hours to make by hand—3D printing takes 5 heures.
- Souvenirs & Gifts: For a music festival, a team printed custom guitar pick souvenirs with attendees’ names. They produced 500 picks in 3 jours, et 95% of attendees said the personalized gift made the festival more memorable.
- Cultural Restoration: The Vatican Museums used 3D printing to restore a broken 16th-century marble statue. They scanned the remaining pieces, rebuilt missing parts (par ex., a cracked hand) in the digital model, then printed the hand in stone-composite material—visitors can’t tell the difference between the original and the 3D printed part.
Le point de vue de Yigu Technology
Chez Yigu Technologie, nous croyons3D printing crafts are bridging the gap between tradition and innovation. Our 3D printers are optimized for craft creators: they support multiple materials (from PLA to ceramics), have a user-friendly interface (no technical expertise needed), and include safety features (par ex., overheat protection) for home use. We’ve helped small businesses cut craft production time by 60% and cultural institutions preserve 200+ fragile relics. As materials improve (par ex., silk-based filaments for luxury crafts), we’ll keep making 3D printing more accessible—so every creator can turn their ideas into art.
FAQ
- Q: What’s the cost of getting started with 3D printing crafts?UN: A beginner-friendly 3D printer costs $200–$500, and PLA filament (the most common material for crafts) is $20–$30 per spool (enough for 5–10 small pieces). No extra tools are needed—just a laptop for modeling software (many free options exist).
- Q: Can 3D printing crafts match the “handmade” feel that many people love?UN: Oui! Post-traitement (papier de verre, peinture, hand-finishing) adds a tactile, artisanal touch. Many 3D printed crafts are mistaken for handmade—for example, 3D printed ceramic mugs with hand-painted designs.
- Q: How long does it take to learn 3D printing for crafts?UN: Beginners can learn to create simple crafts (par ex., un porte-clés) dans 1 à 2 semaines. Mastering complex designs (par ex., sculptures) takes 1–3 months, but free online tutorials (YouTube, Tinkercad’s lessons) speed up the process.