En el acelerado mundo manufacturero actual, ¿Cómo los diseñadores convierten ideas descabelladas en tangibles?, objetos de alto rendimiento? The answer lies in 3D printing creative models—a technology that blends design freedom, flexibilidad de materiales, y personalización para redefinir lo que es posible. Este artículo analiza cómo estos modelos resuelven los puntos débiles de la industria., sus ventajas clave, usos del mundo real, and what the future holds.
What Exactly Are 3D Printing Creative Models?
A 3D printing creative model is a unique three-dimensional object crafted via 3D printing technology, designed to go beyond the limits of traditional manufacturing. Unlike conventional methods (p.ej., moldeo por inyección) that require expensive molds and struggle with complex shapes, these models start as digital designs and are built layer by layer—turning creativity into reality with minimal constraints.
5 Core Advantages of 3D Printing Creative Models
Why are more industries adopting 3D printing creative models? Below is a table highlighting their biggest benefits, along with how they solve common problems:
| Ventaja | How It Solves Problems | Ejemplo del mundo real |
| High Design Freedom | Eliminates “unprintable” shapes; lets designers create organic or geometric structures. | An architect designing a curved building facade—no need to simplify the design. |
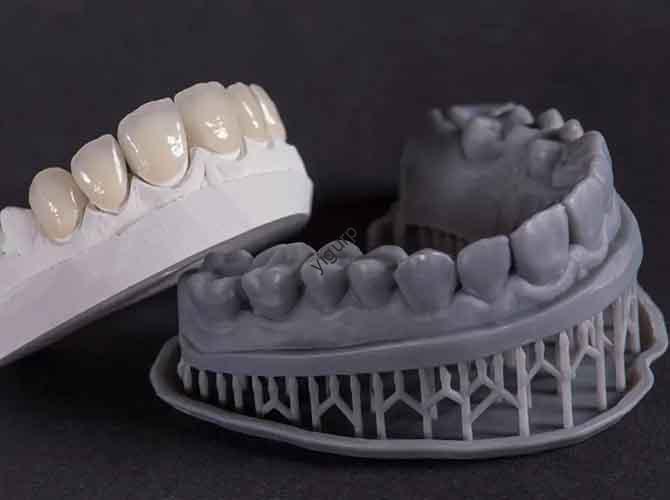
| Material Diversity | Matches materials to model needs (fortaleza, flexibilidad, apariencia). | A dentist using biocompatible resin to print a custom tooth crown. |
| Creación rápida de prototipos | Cuts product development time from weeks to days. | A car company testing 10 different dashboard designs in 3 días (vs. 1 month prior). |
| Personalized Customization | Tailors models to individual user needs (tamaño, función, estilo). | A prosthetics maker creating a leg that fits a patient’s unique body shape. |
| Cost-Effective Small Batches | No mold costs—ideal for 1 to 100-unit production runs. | A startup printing 50 limited-edition phone cases without upfront investments. |
Where Are 3D Printing Creative Models Used?
Their applications span nearly every industry, solving unique challenges in each. Aquí están 4 key sectors with concrete use cases:
- Arquitectura: Architects use 3D printed models to showcase building details (p.ej., marcos de ventanas, staircases) that 2D drawings can’t convey. Por ejemplo, a firm in Berlin printed a 1:50 scale model of a museum—allowing clients to “walk through” the design and spot flaws early.
- Médico: Customization saves lives here. Doctors use patient scans to print 3D-printed implants (p.ej., reemplazos de cadera) or surgical guides. A 2023 study found these models reduce surgery time by 30% on average.
- Aeroespacial: Ligero, complex parts are critical. NASA printed a rocket engine component that was 40% lighter than its metal-cast counterpart—cutting fuel costs for space missions.
- Automotor: Car manufacturers test new parts (p.ej., manijas de las puertas, soportes del motor) quickly. Tesla used 3D printing to prototype a cybertruck component in 24 horas, speeding up its launch by 6 meses.
How Do 3D Printing Creative Models Drive Innovation?
Innovation thrives when ideas can be tested fast—and 3D printing creative models act as a “innovation accelerator.” Here’s a simple 因果链 (cause-effect chain) to explain:
- Designer has an idea → 2. Creates a digital model (1–2 días) → 3. Prints a prototype (horas) → 4. Tests and adjusts (1 día) → 5. Finalizes the product (1 week total).
Compare this to traditional manufacturing:
- Designer has an idea → 2. Creates a mold (2–4 semanas, $10k+) → 3. Produces a prototype (1 semana) → 4. Adjusts the mold (another 2 semanas) → 5. Finalizes the product (2+ months total).
The difference is clear: 3D printing slashes the “idea-to-product” cycle, letting companies iterate faster and stay ahead of competitors.
Future of 3D Printing Creative Models
What’s next for this technology? Industry experts predict three key trends by 2027:
- Material Expansion: More sustainable options (p.ej., recycled plastic, algae-based resin) will become mainstream.
- Faster Printing: New technologies (p.ej., SLA 3.0) will reduce print time for large models by 50%.
- AI Integration: AI will help designers optimize models for strength and cost—e.g., an AI tool that suggests material tweaks to make a part 20% lighter without losing durability.
La perspectiva de la tecnología Yigu
En Yigu Tecnología, we believe 3D printing creative models are not just a tool—they’re a catalyst for democratizing innovation. Small businesses and independent designers now have the same prototyping power as large corporations, leveling the playing field. We’ve seen clients use our 3D printing solutions to launch products (from custom toys to medical devices) in half the time of their competitors. As materials and speed improve, we expect these models to become a standard step in every product’s development journey.
Preguntas frecuentes
- q: How much does it cost to print a 3D creative model?
A: Costs vary by size, material, y complejidad. A small plastic model (p.ej., a keychain) can cost \(5–)20, while a large metal part (p.ej., an aerospace component) may cost \(500–)5,000.
- q: Can 3D printing creative models be used for mass production?
A: They’re best for small batches (1–100 unidades) due to speed limits. Para producción en masa (1,000+ unidades), traditional methods like injection molding are still more cost-effective—though 3D printing is improving for mid-volume runs.
- q: What skills do I need to create a 3D printing creative model?
A: Basic knowledge of 3D design software (p.ej., Tinkercad for beginners, Fusión 360 for advanced users) is enough to start. Many online tutorials (p.ej., YouTube, Coursera) can teach you the basics in 1–2 weeks.