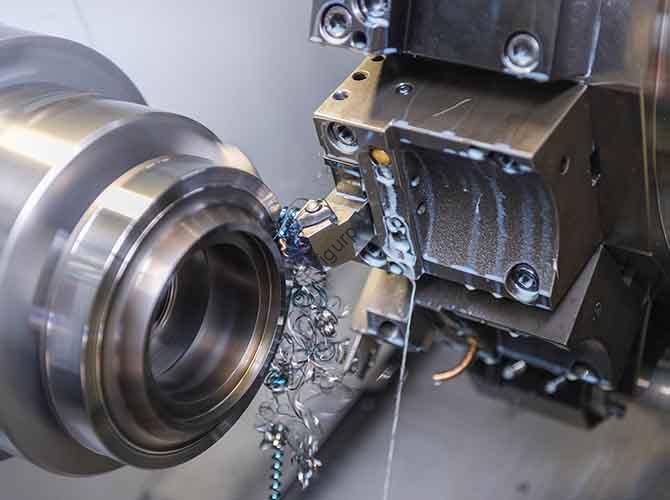
If you’re searching for reliable CNC machining services or looking to partner with manufacturers in Europe, Slovakia stands out as a top choice. With its strategic location in Central Europe, skilled workforce, competitive costs, and strong industrial heritage, Slovakia has become a hub for high-precision CNC machining—serving industries like automotive, Luft- und Raumfahrt, Medizinprodukte, und Elektronik. Whether you need prototype development, Small-Batch-Produktion, oder Großserienfertigung, Slovakia’s CNC machining sector offers the technical expertise and infrastructure to meet strict quality standards, wie ISO 9001 und iatf 16949.
Why Choose CNC Machining in Slovakia? Key Advantages for Businesses
Slovakia’s CNC machining industry isn’t just growing—it’s thriving, thanks to a unique combination of factors that solve common pain points for global buyers, like long lead times, hohe Kosten, or inconsistent quality. Here’s why it’s a smart choice:
Strategic Geographical Location
Slovakia sits at the crossroads of Central Europe, bordering Germany, Austria, Hungary, Polen, and the Czech Republic. This proximity to major European markets (like Germany’s automotive industry) means faster shipping times and lower logistics costs. Zum Beispiel, a CNC part manufactured in Bratislava (Slovakia’s capital) can reach Munich (Deutschland) in gerecht 4 hours by truck, cutting delivery times by 30–50% compared to suppliers in Eastern Europe or Asia. This is critical for industries like automotive, where just-in-time (JIT) production is essential.
Skilled Workforce and Technical Expertise
Slovakia has a long history of engineering excellence, dating back to its days as part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire’s industrial heartland. Heute, the country invests heavily in technical education—with vocational schools and universities (like the Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava) offering specialized programs in CNC programming, Maschinenbau, and precision manufacturing. Laut der Slovak Automotive Industry Association (ZAP) , über 60% of CNC machinists in Slovakia have at least 5 jahrelange Erfahrung, Und 40% hold advanced certifications in CAD/CAM software (Z.B., Solidworks, Mastercam) or CNC machine operation (Z.B., Haas, DMG Mori).
Ein Beispiel in der realen Welt: A German aerospace supplier recently partnered with a Slovak CNC shop to produce complex turbine components. The Slovak team’s expertise in 5-axis machining and ability to work with titanium alloys helped reduce production errors by 25% compared to their previous supplier in Eastern Europe.
Competitive Costs Without Sacrificing Quality
While Western European countries (like Germany or Switzerland) offer top-tier CNC machining, their costs can be 20–35% higher than Slovakia’s. Slovakia’s lower labor and operational costs (combined with access to affordable raw materials from neighboring countries) mean businesses can get high-precision parts at a more budget-friendly price. Zum Beispiel, a custom aluminum CNC part with tight tolerances (± 0,005 mm) might cost €15–€20 in Slovakia, compared to €22–€28 in Germany—without compromising on quality (as most Slovak shops adhere to ISO 9001 und iatf 16949 Standards).
Strong Industrial Ecosystem
Slovakia’s manufacturing sector is well-integrated, with a network of CNC shops, raw material suppliers, and quality testing labs. This means businesses don’t have to source components from multiple countries—they can find everything they need locally. Zum Beispiel, if you need a CNC-machined plastic part, you can work with a Slovak shop that partners with local polymer suppliers (like Slovnaft) and uses in-house CMM (Koordinatenmessmaschine) testing to ensure accuracy. This reduces supply chain complexity and minimizes delays.
How to Select the Right CNC Machining Partner in Slovakia
Choosing the right CNC machining supplier is critical to your project’s success. Mit so vielen Optionen verfügbar, it’s important to focus on factors that align with your specific needs—whether you’re producing automotive parts, Medizinprodukte, or aerospace components. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define Your Project Requirements Clearly
Before reaching out to suppliers, outline key details like:
- Material (Z.B., Aluminium, Stahl, Titan, Plastik)
- Machining processes needed (Z.B., 3-Achse, 5-Achse, Mahlen, drehen)
- Toleranzen (Z.B., ±0.001 mm for precision parts)
- Produktionsvolumen (Prototyp, Kleine Charge <100 Einheiten, large batch >1,000 units)
- Quality standards (Z.B., ISO 9001, Iatf 16949, AS9100 für die Luft- und Raumfahrt)
- Vorlaufzeit (Z.B., 2 Wochen für Prototypen, 6 weeks for large batches)
Zum Beispiel, if you’re developing a medical device component, you’ll need a supplier with ISO 13485 Zertifizierung (für medizinische Geräte) and experience machining biocompatible materials like stainless steel 316L.
2. Verify Certifications and Quality Control Processes
Reputable Slovak CNC shops will hold industry-specific certifications to prove their commitment to quality. Suchen:
- ISO 9001: General quality management (required for most industries)
- Iatf 16949: Specific to automotive manufacturing (critical for parts like engine components)
- AS9100: Für Luft- und Raumfahrtteile (Z.B., Turbinenklingen, Flugzeughalterungen)
- ISO 13485: Für medizinische Geräte (Z.B., chirurgische Instrumente, Implantatkomponenten)
Zusätzlich, ask about their quality control (QC) Prozesse. Do they use CMMs for dimensional testing? Do they perform 100% Inspektion auf kritische Teile, or statistical sampling? A good example is Slovak CNC Solutions (a leading shop in Košice), which uses automated CMMs to check every part before shipping and provides a detailed QC report to clients—giving them peace of mind about accuracy.
3. Evaluate Experience and Specializations
Not all CNC shops are the same—some specialize in specific industries or processes. Zum Beispiel:
- A shop focused on automotive may excel at high-volume production of simple parts (Z.B., Bolzen, Klammern) using 3-axis machines.
- A shop focused on aerospace may specialize in low-volume, Komplexe Teile (Z.B., 5-axis machined turbine housings) using advanced materials like Inconel.
Ask for case studies or references from clients in your industry. Zum Beispiel, if you’re in the electronics sector, a shop that has worked with companies like Samsung or Siemens (which have operations in Slovakia) will understand your need for miniaturized parts with tight tolerances.
4. Assess Technology and Equipment
The quality of a CNC shop’s equipment directly impacts the quality of your parts. Look for shops that invest in modern machinery, wie zum Beispiel:
- 5-Achse CNC Mills (für komplex, 3D-förmige Teile)
- CNC lathes with live tooling (for turning and milling in one setup)
- CAD/CAM-Software (Z.B., Mastercam, Fusion 360) for precise programming
- Automation tools (Z.B., robotic loaders) Für hochvolumige Produktion
A shop with outdated equipment may struggle to meet tight tolerances or fast lead times. Zum Beispiel, a shop using a 10-year-old 3-axis mill may not be able to produce a part with a ±0.002 mm tolerance, whereas a shop with a new DMG MORI 5-axis mill can handle it easily.
5. Compare Costs and Lead Times
Dabei sollten die Kosten nicht der einzige Faktor sein, it’s important to get detailed quotes from 2–3 suppliers. Make sure quotes include:
- Material costs
- Machining labor costs
- Einrichtungsgebühren (for prototypes or small batches)
- Quality testing fees
- Shipping costs (gegebenenfalls)
Auch, confirm lead times upfront. Most Slovak shops can deliver prototypes in 1–2 weeks and large batches in 4–6 weeks, but this can vary based on complexity. Zum Beispiel, a 5-axis machined part with a complex geometry may take 3 Wochen zu produzieren, while a simple turned part can be ready in 5 Tage.
Key Industries Served by Slovakia’s CNC Machining Sector
Slovakia’s CNC machining industry caters to a wide range of sectors, thanks to its versatility and technical expertise. Here are the top industries that rely on Slovak CNC services, along with examples of parts produced:
Automobilindustrie
The automotive sector is Slovakia’s largest industrial employer, with major manufacturers like Volkswagen, Peugeot, and Kia operating factories in the country. CNC machining plays a critical role in producing parts like:
- Motorkomponenten (Z.B., Zylinderköpfe, Kurbelwellen)
- Übertragsteile (Z.B., Getriebe, Wellen)
- Chassis -Komponenten (Z.B., Klammern, Kontrollarme)
Entsprechend ZAP , über 70% of CNC machining revenue in Slovakia comes from the automotive industry. A notable example is Continental Slovakia , a supplier of automotive electronics, which partners with local CNC shops to produce precision sensor housings—requiring tolerances of ±0.003 mm to ensure accurate data collection.
Luft- und Raumfahrt und Verteidigung
Slovakia’s aerospace sector is growing rapidly, with companies like UTC Aerospace Systems (now Collins Aerospace) having a presence in the country. CNC shops in this sector produce high-strength, lightweight parts like:
- Turbinenklingen (using titanium or Inconel)
- Aircraft brackets (Verwendung von Aluminiumlegierung 7075)
- Avionikgehäuse (using magnesium for weight reduction)
These parts require strict adherence to AS9100 standards and often involve 5-axis machining. Zum Beispiel, a Slovak shop in Žilina recently produced 500 turbine blades for a European aircraft manufacturer, using 5-axis mills to achieve the complex airfoil shape and CMM testing to ensure compliance with aerospace regulations.
Medizinprodukte
The medical device industry demands precision and biocompatibility, and Slovak CNC shops meet these needs with ISO 13485 Zertifizierung. Common parts produced include:
- Chirurgische Instrumente (Z.B., Skalpellgriffe, Zange)
- Implantatkomponenten (Z.B., hip implant stems, Zahnabutenten)
- Diagnostic device parts (Z.B., MRI machine brackets)
Eine Fallstudie: A Slovak CNC shop in Bratislava partnered with a German medical device company to produce custom dental abutments. Using 5-axis machining and biocompatible titanium, the shop delivered 1,000 abutments with a tolerance of ±0.002 mm—meeting the strict requirements for dental implants.
Electronics and Telecommunications
With the rise of 5G and IoT devices, the electronics sector needs miniaturized, high-precision CNC parts. Slovak shops produce:
- Leiterplattengehäuse (using plastic or aluminum)
- Connector components (using brass or copper)
- Kühlkörper (using aluminum for thermal conductivity)
Zum Beispiel, a Slovak shop in Banská Bystrica supplies CNC-machined heat sinks to a European 5G equipment manufacturer. The heat sinks, which require precise fin spacing to maximize cooling, are produced using 3-axis mills and undergo 100% inspection to ensure consistency.
Latest Trends Shaping Slovakia’s CNC Machining Industry
Like the global CNC sector, Slovakia’s industry is evolving to keep up with technological advancements and changing market demands. Here are the key trends to watch:
1. Automatisierung und Industrie 4.0 Integration
Slovak CNC shops are increasingly adopting automation to improve efficiency and reduce errors. Dies schließt:
- Robotic loaders: These load and unload parts from CNC machines, zulassen 24/7 operation without human intervention. Zum Beispiel, a shop in Nitra installed robotic loaders on 10 of its CNC lathes, Steigerung der Produktionskapazität durch 40% and reducing labor costs by 25%.
- IoT-connected machines: CNC machines equipped with sensors collect real-time data on performance (Z.B., Spindelgeschwindigkeit, Werkzeugkleidung). This data is analyzed to predict maintenance needs and optimize production. A survey by the Slovak Chamber of Commerce habe das gefunden 60% of mid-sized CNC shops in Slovakia now use IoT-connected machines.
- Digital twins: Some advanced shops use digital twins (virtual replicas of CNC machines) to test machining programs before running them on physical equipment. This reduces setup time and minimizes material waste.
2. 5-Axis Machining for Complex Parts
While 3-axis machining is still common for simple parts, 5-axis machining is becoming the standard for complex components (Z.B., Luft- und Raumfahrt -Turbinenklingen, Medizinische Implantate). 5-axis machines can move a part in five different directions, allowing for the production of intricate geometries in a single setup—reducing lead time and improving accuracy. According to industry data, the number of 5-axis CNC machines in Slovakia has increased by 35% in the past 5 Jahre, as shops look to meet the demands of high-tech industries.
3. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Practices
As global demand for sustainability grows, Slovak CNC shops are adopting eco-friendly measures:
- Abfallreduzierung: Shops are using software to optimize cutting paths, reducing material waste by 15–20%. Zum Beispiel, a shop in Trnava uses Mastercam’s “OptiRough” toolpath to minimize chip production when machining aluminum.
- Energy efficiency: Newer CNC machines are designed to use less energy. A modern 5-axis mill uses 30% less electricity than a machine built 10 years ago.
- Recycled materials: Many shops now offer machining services using recycled metals (Z.B., recycled aluminum, Stahl) to reduce their carbon footprint. Some even partner with local recycling facilities to source materials.
4. Customization and Low-Volume Production
With the rise of on-demand manufacturing, Slovak CNC shops are focusing on customization and low-volume production. This is especially important for startups and small businesses that need prototypes or small batches of parts. Zum Beispiel, a Slovak shop in Prešov offers “rapid CNC machining” services, delivering custom prototypes in as little as 3 days—helping startups bring their products to market faster.
Kostenaufschlüsselung: What to Expect When Outsourcing CNC Machining to Slovakia
Understanding the cost structure of CNC machining in Slovakia helps you budget effectively and avoid unexpected expenses. Below is a typical cost breakdown for common projects, based on data from Slovak CNC shops and industry reports:
| Projekttyp | Material | Bearbeitungsvorgang | Volumen | Average Cost per Unit | Vorlaufzeit | Key Cost Treiber |
| Prototyp (simple part) | Aluminium 6061 | 3-Achsfräsen | 1–5 Einheiten | €8–€15 | 1–2 Wochen | Einrichtungsgebühren, small volume |
| Small-batch (Automobil) | Stahl 1018 | CNC drehen sich | 50–100 Einheiten | €5–€8 | 2–3 Wochen | Arbeit, Materialkosten |
| Large-batch (Elektronik) | Plastik (ABS) | 3-Achsfräsen | 1,000+ Einheiten | €1.50–€3.00 | 4–6 Wochen | Automatisierung (robotic loaders), Mengenrabatte |
| Komplexer Teil (Luft- und Raumfahrt) | Titanti-6Al-4V | 5-Achsfräsen | 20–50 Einheiten | €50–€80 | 3–4 Wochen | Advanced material, 5-axis setup, quality testing |
Factors That Affect Cost
- Materialauswahl: Titanium and Inconel are more expensive than aluminum or steel. Zum Beispiel, titanium costs €8–€12 per kg, while aluminum costs €2–€3 per kg.
- Teilkomplexität: 5-axis machining costs more than 3-axis because it requires more advanced equipment and programming. A complex 5-axis part can cost 2–3 times more than a simple 3-axis part.
- Toleranzen: Engere Toleranzen (Z.B., ± 0,001 mm) require more precise machining and longer setup times, steigende Kosten. A part with ±0.001 mm tolerance can cost 50% more than one with ±0.01 mm tolerance.
- Volumen: Larger volumes lead to lower per-unit costs, as setup fees are spread across more parts. Zum Beispiel, a part that costs €15 for 1 unit may cost €5 for 100 Einheiten.
Compliance and Regulations for CNC Machining in Slovakia
To ensure your project meets legal and industry standards, it’s important to understand the regulations governing CNC machining in Slovakia:
Qualitätsstandards
Wie bereits erwähnt, most Slovak CNC shops hold international quality certifications:
- ISO 9001: Mandatory for most B2B projects, as it ensures consistent quality management.
- Iatf 16949: Required for automotive parts, as it aligns with global automotive standards (Z.B., those set by Ford, General Motors, Toyota).
- AS9100: Required for aerospace parts, as it meets the strict safety and quality requirements of the aerospace industry.
- ISO 13485: Required for medical devices, as it ensures parts are safe for human use and meet regulatory requirements (Z.B., EU MDR—Medical Device Regulation).
Umweltvorschriften
Slovakia adheres to EU environmental laws, which govern waste disposal, emissions, and energy use. CNC shops must comply with:
- EU Waste Framework Directive: Requires shops to recycle or properly dispose of machining waste (Z.B., metal chips, Öl). Most shops partner with licensed waste management companies to ensure compliance.
- EU Emissions Trading System (ETS): Applies to large shops that emit significant amounts of CO2. Smaller shops are exempt but still need to meet local air quality standards.
- Energy Efficiency Directive: Encourages shops to use energy-efficient equipment and reduce their carbon footprint.
Import/Export Rules
If you’re importing CNC parts from Slovakia to another country, or exporting materials to Slovakia for machining, you’ll need to comply with:
- EU Customs Union: Parts shipped within the EU don’t require customs duties or additional paperwork—simplifying cross-border transactions. Zum Beispiel, a French automotive company can import CNC-machined engine parts from Slovakia without paying tariffs, reducing overall costs.
- Non-EU Exports: If shipping parts to countries outside the EU (Z.B., the U.S., China), you’ll need to provide a Certificate of Origin to prove the parts were manufactured in Slovakia. This can help reduce or eliminate import duties in the destination country (depending on trade agreements). Zum Beispiel, parts exported to the U.S. may qualify for reduced tariffs under the EU-U.S. Trade and Technology Council (TTC) initiatives.
- Restricted Materials: Some materials used in CNC machining (Z.B., certain titanium alloys for aerospace) may be subject to export controls. Ensure your supplier has the necessary licenses if you’re working with restricted materials—this avoids delays or legal issues.
Yigu Technology’s Perspective on CNC Machining in Slovakia
As a company with extensive experience in global manufacturing and supply chain management, Yigu Technology recognizes Slovakia as a standout destination for CNC machining in Europe. What sets Slovakia apart is its rare balance of technical excellence and cost efficiency—two factors that are often mutually exclusive in Western or Eastern Europe.
We’ve observed that Slovak CNC shops excel at adapting to diverse industry needs, whether it’s high-volume automotive parts or low-volume, complex aerospace components. Their integration of Industry 4.0 Werkzeuge (like IoT-connected machines and digital twins) also aligns with the global shift toward smart manufacturing, making them reliable long-term partners for businesses looking to scale.
Zusätzlich, Slovakia’s commitment to sustainability resonates with our focus on eco-friendly supply chains. The adoption of recycled materials and energy-efficient machining helps reduce the carbon footprint of production—an increasingly important factor for clients worldwide. For businesses seeking to optimize their manufacturing processes, Slovakia’s CNC sector offers a practical, future-forward solution.
FAQ: Common Questions About CNC Machining in Slovakia
1. What is the average lead time for CNC machining projects in Slovakia?
Die Führungszeiten variieren je nach Projektkomplexität und Volumen. Für einfache Prototypen (1–5 Einheiten), most shops deliver in 1–2 Wochen. Kleine Chargen (50–100 Einheiten) typically take 2–3 Wochen, while large batches (1,000+ Einheiten) or complex 5-axis parts may require 3–6 Wochen. Rush services are often available for urgent projects, with prototypes sometimes delivered in as little as 3 Tage (gegen eine zusätzliche Gebühr).
2. Do Slovak CNC shops offer design support or CAD/CAM services?
Ja, many reputable shops provide design support, including CAD modeling and CAM programming. This is especially helpful for businesses that have a concept but need help refining the design for manufacturability (DFM). Zum Beispiel, if you have a 2D drawing of a part, a Slovak shop can convert it to a 3D CAD model and optimize the design to reduce machining time and costs.
3. Can Slovak CNC shops handle large-scale production (10,000+ Einheiten)?
Absolut. While some shops specialize in prototypes or small batches, many mid-sized to large Slovak CNC facilities are equipped for high-volume production. They use automation tools like robotic loaders and conveyor systems to handle 10,000+ unit orders efficiently. Zum Beispiel, a shop in Bratislava with 20+ CNC lathes and mills regularly fulfills large orders for automotive clients, with monthly production volumes exceeding 50,000 Teile.
4. What quality documentation do Slovak CNC shops provide?
Most shops offer detailed quality documentation, einschließlich:
- First Article Inspection (Fai) Reports: For new projects, to verify the first part meets all specifications.
- Koordinatenmessmaschine (CMM) Reports: To prove dimensional accuracy (with measurements down to ±0.001 mm).
- Material Certificates (Mill Test Reports): To confirm the material used meets industry standards (Z.B., ASTM, IN).
- ISO Compliance Certificates: To validate adherence to quality standards like ISO 9001 oder IATF 16949.