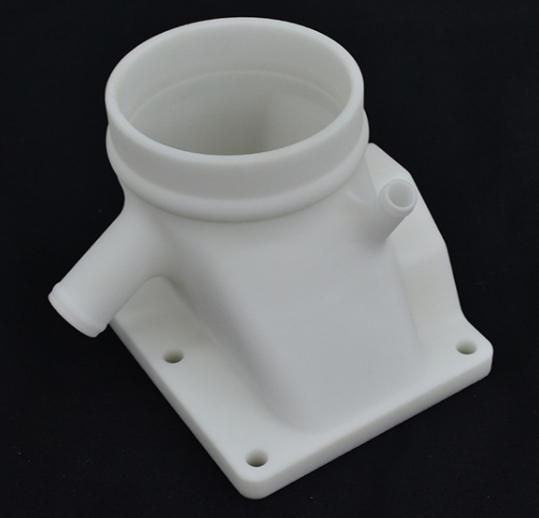
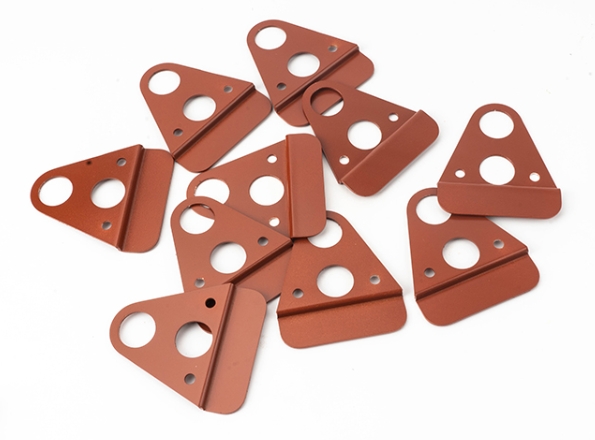
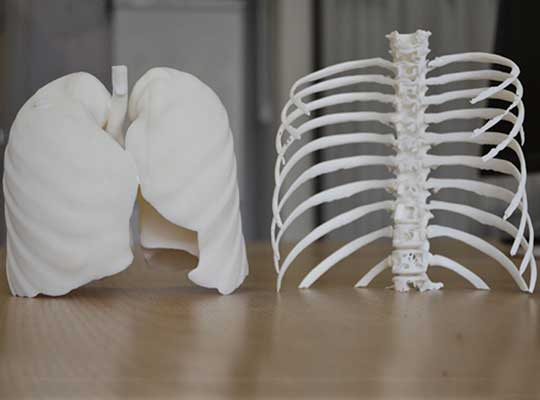
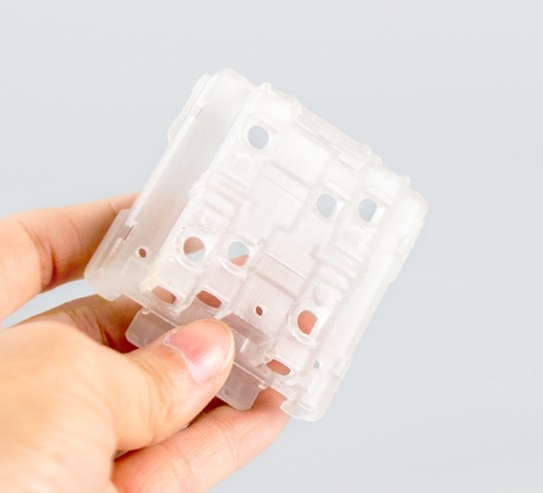
If you work in product development or manufacturing, understanding how أجزاء النموذج الأولي differ from machined parts is key to avoiding costly mistakes. These two manufacturing outputs serve entirely distinct stages of production—one focuses on testing ideas, while the other delivers consistent, production-ready components. أقل, we break down their differences with clear data, أمثلة, and actionable insights to help you choose the right option for your project.
1. Core Production Goal: Testing Ideas vs. Mass Supply
The biggest divide between prototype parts and machined parts lies in their purpose. Prototype parts are built to validate designs, while machined parts are made to meet industrial production needs.
| وجه | أجزاء النموذج الأولي | Machined Parts |
| Primary Objective | تحقق من جدوى التصميم; fix flaws early | Produce consistent parts for assembly or sale |
| Target Stage | Product development (pre-production) | إنتاج متسلسل (post-design finalization) |
| End-User | Design teams, المستثمرون, testing departments | Manufacturers, assembly lines, end customers |
| Typical Output | 1–10 pieces per design (صغير, iterative batches) | 100–10,000+ pieces per order (كبير, uniform runs) |
على سبيل المثال, if you’re developing a new laptop hinge, you’d first create 3–5 أجزاء النموذج الأولي to check if the hinge opens smoothly and holds the screen securely. Once the design works, you’d make 5,000 machined parts to install in production laptops.
2. Manufacturing Technologies: المرونة مقابل. دقة
Prototype parts use diverse, fast methods to test designs, while machined parts rely on specialized techniques for consistent quality.
Prototype Part Technologies (سريع, Adaptable)
- 3د الطباعة: Turns digital designs into physical parts in 4–24 hours; ideal for complex shapes (على سبيل المثال, custom smartphone cases).
- تصنيع CNC: Uses computer-controlled tools to carve parts from solid materials; great for testing strength (على سبيل المثال, أقواس معدنية).
- اليدين: Manual work with tools like drills or sanders; perfect for quick tweaks (على سبيل المثال, adjusting the size of a plastic prototype).
- Key benefit: These methods let you modify designs in days—no need for expensive setup changes. على سبيل المثال, a 3D printed prototype can be revised and reprinted in under 12 ساعات.
Machined Part Technologies (Precise, Scalable)
- Turning: Spins materials while cutting tools shape them; used for cylindrical parts (على سبيل المثال, bolts, pipes).
- Milling: Uses rotating cutters to remove material from a workpiece; makes flat or complex 3D shapes (على سبيل المثال, laptop chassis).
- Grinding: Uses abrasive wheels to smooth surfaces; ensures ultra-tight tolerances (على سبيل المثال, مكونات الجهاز الطبي).
- Key benefit: These techniques achieve precision within ±0.001 inches—critical for parts that need to fit together perfectly (like engine components). زيادة 70% of industrial machined parts use turning or milling for consistency.
3. Key Characteristics: Uniqueness vs. تناسق
Prototype parts are designed to be one-of-a-kind for testing, while machined parts must meet strict, uniform standards for mass production.
Prototype Part Characteristics
- Diversity: Each prototype can be different. على سبيل المثال, you might make one plastic prototype and one metal prototype of a tool handle to test weight and grip.
- Iterativity: They’re meant to be modified. 85% of product teams revise prototypes 2–4 times to fix issues like poor fit or weak spots.
- Non-Production Focus: They don’t need to meet long-term durability standards. A prototype of a water bottle might only be tested for shape—no need to check if it resists cracking after 100 يستخدم.
Machined Part Characteristics
- دقة: Every part must match exact specs. A batch of machined bolts, على سبيل المثال, must all have the same thread size (على سبيل المثال, M8 x 1.25mm) to fit into nuts.
- تناسق: 99% of machined parts in a batch are identical. This is vital for assembly lines—if one part is too big, it can stop production.
- Production Readiness: They’re built to last. Machined parts for cars, for instance, must withstand heat, اهتزاز, and wear for years.
4. مقارنة التكلفة: الاستثمار على المدى القصير مقابل. Long-Term Value
Costs differ because prototype parts prioritize speed over scale, while machined parts leverage volume to lower per-unit costs.
انهيار التكلفة (ل 50 Pieces of a Small Metal Part)
| نوع التكلفة | أجزاء النموذج الأولي (3D Printed + CNC) | Machined Parts (Milling + Turning) |
| Setup Cost | \(100- )300 (no specialized tooling) | \(500- )1,200 (tooling and programming) |
| تكلفة لكل قطعة | \(15- )40 | \(3- )8 |
| Total Cost for 50pcs | \(750- )2,000 + \(100- )300 = \(850- )2,300 | \(150- )400 + \(500- )1,200 = \(650- )1,600 |
- When prototypes are cheaper: For 1–20 pieces. إذا كنت بحاجة 10 أجزاء, تكلفة النماذج الأولية \(150- )400 total—far less than machined parts (\(500- )1,200 setup + \(30- )80 أجزاء).
- When machined parts are cheaper: ل 100+ قِطَع. ل 200 أجزاء, machined parts cost \(600- )1,600 + \(500- )1,200 = \(1,100- )2,800, while prototypes cost \(3,000- )8,000.
منظور Yigu Technology
في Yigu Technology, we view أجزاء النموذج الأولي as the “design safety net” and machined parts as the “production backbone.” For prototypes, we use 3D printing and CNC machining to deliver iterations in 3–5 days, helping clients catch flaws early (like a poorly fitting gear) before investing in tooling. For machined parts, our precision turning and milling processes ensure 99.5% consistency—critical for clients in automotive and electronics. By combining these two, we help teams move from idea to mass production faster and more affordably.
التعليمات
- Can machined parts be used as prototypes?
نعم, but it’s costly. Machined parts require tooling, so making 1–5 as prototypes would cost \(500- )1,200 in setup fees—far more than 3D printed prototypes (\(100- )300). Save machined parts for after design finalization.
- How do I know if I need a prototype or a machined part?
If you’re still testing design changes (على سبيل المثال, adjusting a part’s size), use a prototype. If your design is fixed and you need 50+ identical parts for production, use a machined part.
- Are prototype parts less durable than machined parts?
Not always, but they’re not built for long-term use. A CNC machined prototype can be as durable as a production machined part, but a 3D printed prototype (made of PLA plastic) may break easily—choose prototype materials based on your test needs.