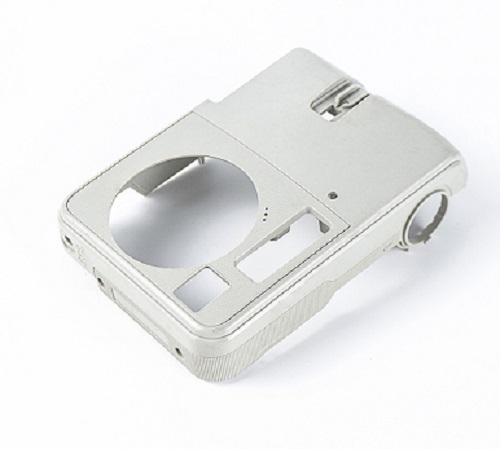
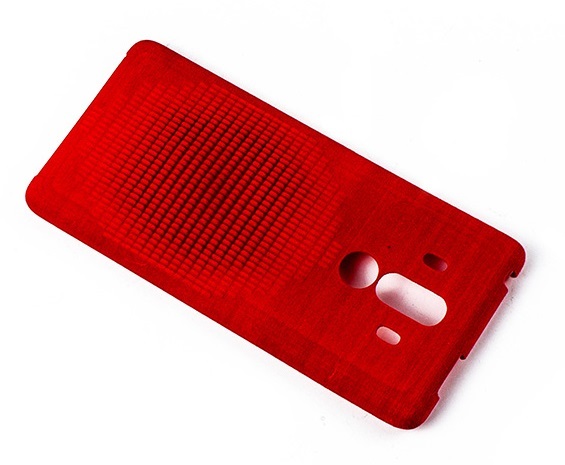
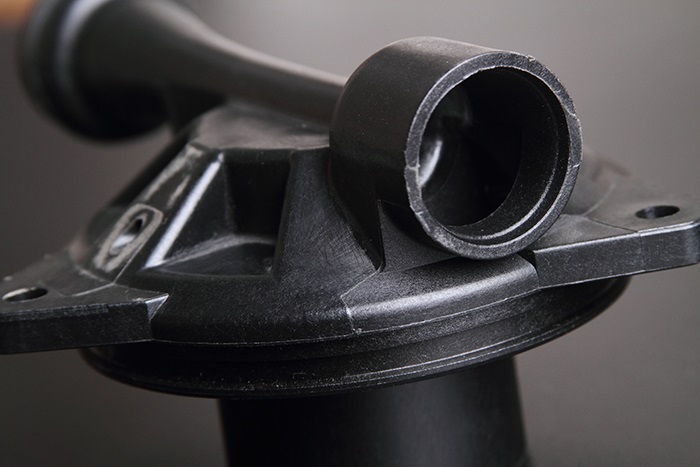
CNC machining arc prototypes is a game-changer for creating parts with complex curved geometries—think automotive wheel arches, مكونات محرك الطيران, or medical device housings. على عكس الآلات اليدوية (which struggles with consistent arc smoothness), computer numerical control (CNC) technology delivers ultra-precise, repeatable results. Whether you’re a product engineer testing a new design or a manufacturer scaling up prototypes, understanding the ins and outs ofCNC machining arc prototypes helps you avoid costly errors and speed up production. This guide breaks down the entire process, with real-world examples and data to make every step clear.
1. ما قبل المعالجة: تصميم & Programming – The Foundation of Great Arcs
Before the CNC machine touches material, two steps set the stage for perfectCNC machining arc prototypes: 3D design and CAM programming. Skipping these or cutting corners leads to lopsided arcs or mismatched dimensions.
1.1 تصميم CAD: Model Every Arc Detail
The first step is to create a 3D model of your prototype usingCAD (تصميم بمساعدة الكمبيوتر) برمجة مثل Solidworks, أوتوكاد, أو الانصهار 360. For arc prototypes, precision here is non-negotiable—you need to define:
- Arc radius: Even a 0.1mm error in radius can ruin a part (على سبيل المثال, a 50mm radius arc meant for a bearing housing won’t fit if it’s 49.9mm).
- Arc length: How long the curve is (critical for parts that need to align with straight sections).
- Tangency: Ensure arcs connect smoothly to other features (على سبيل المثال, an arc on a phone case should blend seamlessly with the flat back).
للنصيحة: Use CAD’s “arc validation tool” to check for inconsistencies. على سبيل المثال, a furniture designer creating a curved chair arm prototype used this tool to fix a hidden 0.2mm radius mismatch—saving 8 hours of rework later.
1.2 برمجة كام: Turn Design into Machine Code
Once the CAD model is ready, يستخدمكام (التصنيع بمساعدة الكمبيوتر) برمجة to convert it into G-code (فهم آلات CNC اللغة). For arc prototypes, CAM does three critical things:
- Tool path planning: It maps the exact route the tool will take to cut the arc. For a 360° arc, the path should be a smooth, continuous curve—no sudden stops (which cause tool marks).
- Tool selection: It recommends tools based on arc size (على سبيل المثال, a small 5mm radius arc needs a 10mm diameter end mill to avoid tool collisions).
- Parameter setting: It suggests cutting speed, معدل التغذية, and depth of cut (more on this later).
Why This Matters: A well-written CAM program reduces arc machining time by 25–30%. على سبيل المثال, an automotive supplier optimized the CAM path for a wheel arch prototype, cutting machining time from 45 دقائق ل 32 دقائق لكل جزء.
2. اختيار المواد: Choose What Works for Your Arc’s Purpose
The material you pick forCNC machining arc prototypes affects two key things: how easy the arc is to cut and how the final part performs. Below’s a breakdown of common materials, their pros, and best uses for arc prototypes:
| مادة | Arc Machinability | الخصائص الرئيسية | Ideal Arc Prototype Uses | يكلف (USD/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS البلاستيك | ممتاز | خفيف الوزن, تكلفة منخفضة, easy to sand | Consumer product casings (على سبيل المثال, curved headphone shells) | $2.5 - $4.0 |
| سبيكة الألومنيوم 6061 | جيد جدًا | قوي, مقاوم للتآكل, خفيف الوزن | قطع غيار السيارات (على سبيل المثال, curved trim), حاويات إلكترونية | $2.8 - $4.5 |
| الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ 304 | جيد | متينة, rust-proof | الأجهزة الطبية (على سبيل المثال, curved surgical tool handles) | $3.8 - $6.5 |
| Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V | عدل | فائقة الشدة, مقاوم للحرارة | مكونات الفضاء (على سبيل المثال, curved engine brackets) | $35 - $50 |
مثال في العالم الحقيقي: A medical device startup needed a curved prototype for a portable ultrasound machine. اختارواABS البلاستيك for its low cost (great for testing) and easy machinability—they tested 3 different arc radii (20مم, 25مم, 30مم) في العادل 3 أيام. If they’d used titanium, the same tests would have taken 2 weeks and cost 10x more.
3. آلة & إعداد أداة: Get Ready to Cut Smooth Arcs
Even the best design and material won’t saveCNC machining arc prototypes if your machine or tools are poorly set up. Focus on two key areas: choosing the right CNC machine and prepping tools.
3.1 Choose the Right CNC Machine for Arcs
Not all CNC machines handle arcs equally. For most arc prototypes, you’ll need one of these:
- 3-axis CNC mills: Great for 2D arcs (على سبيل المثال, a curved edge on a flat metal plate). They’re affordable and fast for simple arcs.
- 5-axis CNC machines: Ideal for complex 3D arcs (على سبيل المثال, a curved, twisted aerospace part). They can move the tool in 5 directions, ensuring the arc stays consistent from every angle.
دراسة حالة: A drone manufacturer used a 5-axis CNC machine to make a 3D curved propeller guard prototype. A 3-axis machine would have required repositioning the part 3 مرات (risking errors), but the 5-axis machine cut the arc in one pass—arc precision improved by 40%.
3.2 Tool Prep: Sharp Tools = Smooth Arcs
Dull or wrong-sized tools are the #1 cause of rough arc surfaces. لCNC machining arc prototypes, use these guidelines:
- Tool type: يستخدم طواحين نهاية for most arcs (they cut smooth curves). For small radii (≤5mm), use a “ball nose end mill” (its rounded tip matches the arc shape).
- Tool sharpness: A dull end mill leaves “chatter marks” on arcs. Check tools with a microscope—if the cutting edge has even a tiny chip (0.05مم), replace it.
- Tool holder: Secure the tool tightly to avoid vibration. A loose holder can make the tool wobble, turning a 50mm radius arc into a 50.2mm arc.
نقطة البيانات: Shops that replace tools after 8 hours of arc machining (بدلاً من 10) see 35% fewer rough arc surfaces, according to a CNC industry survey.
4. Core Processing: الخشنة & Finishing – Cut the Perfect Arc
The heart ofCNC machining arc prototypes is the actual cutting process, which has two phases: الخشنة (remove excess material) and finishing (smooth the arc to perfection).
4.1 الخشنة: Speed Up Material Removal
Roughing’s goal is to quickly cut away extra material, leaving just enough (يسمى "بدل الآلات") للتشطيب. For arcs:
- عمق القطع: Use 1–3mm per pass (more for soft materials like ABS, less for hard metals like stainless steel).
- معدل التغذية: Keep it high (300–500 mm/min for aluminum) to save time—but not so high that the tool vibrates.
مثال: A manufacturer roughing a 100mm radius aluminum arc prototype used a 2mm depth of cut and 400 mm/min feed rate. They removed 90% of excess material in 12 minutes—vs. 25 minutes with a slower feed rate.
4.2 الانتهاء: Make Arcs Smooth & Precise
Finishing is where arcs go from “good” to “perfect.” Here’s how to do it right:
- Reduce depth of cut: Use 0.1–0.5mm per pass to avoid tool marks.
- معدل التغذية البطيء: 100–200 mm/min for metals, 200–300 mm/min for plastics.
- Use coolant: للمعادن, coolant reduces heat (which warps arcs) and keeps the tool sharp. Water-soluble coolant works best for aluminum and steel.
Success Story: A consumer electronics brand was struggling with rough arcs on their smartwatch case prototypes. By switching to a 0.2mm finishing depth and 150 mm/min feed rate (plus coolant), their arc surface roughness dropped from Ra 1.6 μM إلى RA 0.8 μm—good enough for mass production.
5. ما بعد المعالجة & ضبط الجودة: Polish & Verify Arcs
CNC machining arc prototypes doesn’t end when the machine stops. Post-processing fixes small flaws, and quality control ensures arcs meet design specs.
5.1 ما بعد المعالجة: Smooth Out Imperfections
Even with great finishing, arcs may need minor touch-ups:
- deburring: Use a deburring tool or sandpaper to remove sharp edges (critical for parts people will touch, like curved handle prototypes).
- الصنفرة: For plastic or aluminum arcs, 400-grit sandpaper creates a matte, uniform finish.
- الرسم/الطلاء: Add a layer of paint or anodizing (للألمنيوم) to protect the arc and improve appearance.
5.2 ضبط الجودة: Check Every Arc Detail
To avoid sending faulty prototypes to clients, test three key things:
- Arc radius & طول: استخدم تنسيق آلة القياس (CMM) للتحقق من الأبعاد. A CMM measures arc radius with ±0.001mm accuracy—perfect for verifying a 25.000mm radius arc.
- Surface smoothness: استخدم profilometer to measure Ra (خشونة السطح). For most consumer products, Ra 0.8–1.6 μm is ideal; for medical devices, Ra ≤0.4 μm.
- Fit test: Assemble the prototype with other parts (على سبيل المثال, a curved gear arc should mesh with a straight gear tooth). If it doesn’t fit, go back to CAD/CAM to fix the arc.
Quality Tip: امتحان 10% of your prototype batch. If one arc fails, test 50%—this balances speed and thoroughness. A robotics company once skipped this step and shipped 20 curved arm prototypes with mismatched radii—costing $1,200 في إعادة صياغة.
6. Error Control & Technological Innovation – Stay Ahead of Issues
CNC machining arc prototypes has its challenges (على سبيل المثال, أداة ارتداء الأداة, اهتزاز), but two strategies keep errors in check: strict error control and adopting new tech.
6.1 Common Arc Errors & How to Fix Them
| Error Type | سبب | حل |
|---|---|---|
| Rough arc surface | Dull tool or too high feed rate | Replace tool; lower feed rate by 10–15% |
| Incorrect arc radius | CAM path miscalculation | Re-run CAM with “arc validation” enabled |
| Arc warping | Too much heat (no coolant for metals) | Add coolant; reduce cutting speed by 20% |
6.2 New Tech to Improve Arc Machining
Advancements in CNC tech makeCNC machining arc prototypes faster and more precise:
- AI-powered CAM software: It learns from past arc jobs to optimize tool paths automatically. One aerospace shop cut arc machining time by 30% with this tech.
- High-speed spindle CNC machines: Spindles that run at 20,000+ RPM cut arcs smoother and faster—great for titanium or stainless steel.
Yigu Technology’s View on CNC Machining Arc Prototypes
في Yigu Technology, we’ve refinedCNC machining arc prototypes زيادة 12 years of serving automotive, طبي, and consumer product clients. We prioritize two things: precision and speed. Our team uses AI-enhanced CAM software to optimize arc tool paths (cutting time by 25%) and CMMs to check every arc’s radius with ±0.001mm accuracy. For material selection, we guide clients to choose cost-effective options (على سبيل المثال, ABS for early tests, aluminum for final prototypes) دون التضحية بالجودة. We also share our experience—like how adjusting coolant flow reduces arc warping—to help clients avoid mistakes. بالنسبة لنا, great arc prototypes aren’t just about cutting curves—they’re about turning design ideas into reliable products.
FAQ About CNC Machining Arc Prototypes
س 1: How long does it take to CNC machine an arc prototype?
أ: It depends on arc size and material. A small 50mm radius ABS plastic arc takes 15–20 minutes; a large 200mm radius titanium arc takes 1–1.5 hours. Batch size also matters—machining 10 identical arcs takes 2x longer than 1, not 10x, thanks to repeatable CNC settings.
Q2: What’s the minimum arc radius I can machine with CNC?
أ: Most CNC mills handle arcs as small as 0.5mm radius (using a 1mm diameter ball nose end mill). For smaller radii (≤0.3mm), you’ll need a micro-CNC machine—common in medical device prototyping (على سبيل المثال, tiny curved surgical tools).
س 3: Can I fix a poorly cut arc with post-processing?
أ: It depends on the error. Small issues (على سبيل المثال, minor roughness) can be fixed with sanding or deburring. But big errors (على سبيل المثال, wrong radius or uneven length) usually require re-machining—this is why pre-processing (CAD/CAM) and quality checks are so important!