CNC finishing prototype is a high-precision machining process that uses computer numerical control (CNC) technology to refine prototypes or parts, creating near-final products for testing and validation. It plays a critical role in the late stages of product development—helping teams check functionality, مظهر, and dimensional accuracy before mass production. This guide covers every key step to master CNC finishing prototypes, with practical tips and real-world examples.
1. Design and Programming: وضع الأساس للدقة
The first step in creating a CNC finishing prototype is to build a detailed 3D model and convert it into machine-readable code. This stage directly affects the final prototype’s accuracy.
Key Design & Programming Steps
- 3D النمذجة مع برنامج CAD: Use professional tools like Solidworks, أوتوكاد, أو و to design the prototype’s 3D model. Ensure every detail—from small holes to surface curves—matches the final product’s requirements. على سبيل المثال, if designing a plastic electronic enclosure, include 0.5mm-thick walls and M3 screw holes in the model.
- Convert to CNC Code via CAM Software: Import the 3D model into CAM software (على سبيل المثال, Mastercam, الانصهار 360). The software generates G-code (فهم آلات CNC اللغة) and defines:
- مسار الأداة: The route the cutting tool takes to avoid collisions and ensure smooth machining.
- قصات القطع: سرعة (دورة في الدقيقة), معدل التغذية (مم/دقيقة), and depth of cut—tailored to the material (على سبيل المثال, slower speed for stainless steel).
قضية: A consumer electronics company needed a CNC finishing prototype of a smartphone charger shell (ABS material). Engineers used SolidWorks to model the 60x40x20mm shell with 0.8mm-thick walls and two USB port cutouts. They then used Mastercam to set a tool path that first machined the outer shape, then the inner ports, and set a feed rate of 500mm/min—resulting in a prototype that matched the design within ±0.02mm.
2. Material Selection and Preparation: Choose the Right Base
Selecting and preparing the right material is vital for a successful CNC finishing prototype. The material must balance mechanical performance (قوة, المرونة) وقابلية المعالجة (ease of cutting).
جدول مقارنة المواد
| نوع المواد | المزايا الرئيسية | الأفضل ل | صعوبة الآلات | يكلف (لكل كجم) |
| ABS البلاستيك | سهل الجهاز, تكلفة منخفضة, مقاومة تأثير جيد | Consumer goods prototypes (على سبيل المثال, قطع غيار, حاويات) | قليل | \(15- )25 |
| جهاز الكمبيوتر البلاستيكي | مقاومة حرارة عالية, شفاف, جامد | Prototypes for high-temperature use (على سبيل المثال, LED light covers) | واسطة | \(20- )35 |
| سبيكة الألومنيوم (6061) | خفيف الوزن, قوي, إنهاء سطح جيد | الأجزاء الصناعية (على سبيل المثال, mechanical brackets) | قليل | \(30- )45 |
| الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ (304) | مقاوم للتآكل, متينة | Prototypes for harsh environments (على سبيل المثال, أدوات المطبخ) | عالي | \(50- )70 |
نصائح التحضير
- فحص الجودة: Check materials for defects (على سبيل المثال, cracks in plastic, dents in metal) قبل الآلات. A defective material can break the cutting tool or ruin the prototype—reject 100% of materials with visible flaws.
- Cut to Size: Trim the raw material to a slightly larger size than the prototype (على سبيل المثال, add 5mm to each dimension). This gives the CNC machine enough material to remove during roughing.
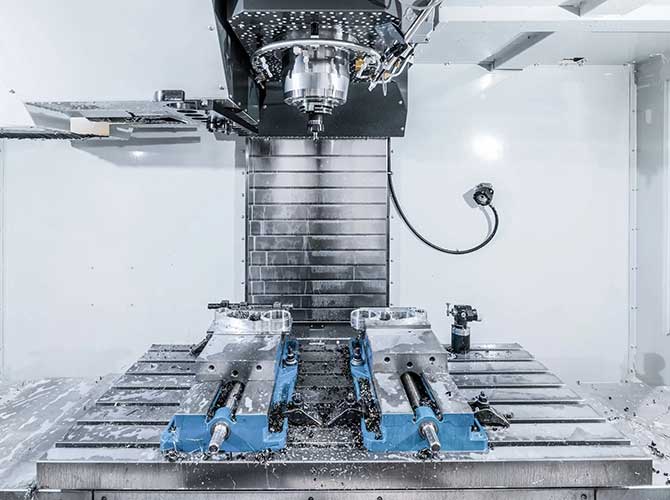
3. Precision Machining Equipment: Use the Right Tools
High-precision CNC machines are non-negotiable for CNC finishing prototypes. The type of machine depends on the prototype’s shape and complexity.
Common CNC Machines for Finishing Prototypes
| نوع الآلة | الأفضل ل | دقة الآلات | Typical Use Case |
| CNC Milling Machine | Flat or 3D-shaped prototypes (على سبيل المثال, حاويات, قوسين) | ± 0.01mm | Machining an aluminum alloy phone stand |
| CNC Lathe | Cylindrical prototypes (على سبيل المثال, البراغي, الأنابيب) | ± 0.005mm | Finishing a stainless steel water bottle neck |
Maintenance Tips
- Regular Calibration: Calibrate the machine every 2 weeks using a laser interferometer to check axis accuracy. This ensures the machine doesn’t drift from its original precision.
- Tool Maintenance: Sharpen cutting tools (على سبيل المثال, طواحين نهاية, تدريبات) بعد 10 ساعات من الاستخدام. Dull tools cause rough surfaces and increase machining time.
4. The Machining Process: الخشنة مقابل. الانتهاء
CNC finishing prototypes involve two key stages—roughing and finishing—to balance speed and precision.
خطوة 1: Roughing Stage
- هدف: Remove most excess material quickly to form the prototype’s basic shape.
- أدوات & حدود: Use a large-diameter cutting tool (على سبيل المثال, 10mm end mill) and a deep depth of cut (على سبيل المثال, 2مم لكل تمريرة) لتوفير الوقت. على سبيل المثال, roughing an aluminum bracket from a 100x80x50mm block to 80x60x30mm in 10 دقائق.
خطوة 2: Finishing Stage
- هدف: Achieve the final dimensions and smooth surface roughness (قيمة RA).
- أدوات & حدود: Use a small-diameter tool (على سبيل المثال, 3mm end mill) and a shallow depth of cut (على سبيل المثال, 0.1مم لكل تمريرة). Lower the feed rate (على سبيل المثال, 300mm/min for plastic) to avoid tool vibration. على سبيل المثال, finishing the aluminum bracket to 78x58x28mm with an Ra of 0.8μm (smooth enough for painting).
5. Post-Processing and Inspection: Polish and Validate
بعد الآلات, post-processing enhances the prototype’s appearance, while inspection ensures it meets standards.
خطوات ما بعد المعالجة
- deburring: Use a file or sandpaper (400# حصى) to remove sharp edges and burrs—critical for prototypes that users will touch (على سبيل المثال, قطع غيار).
- تلميع: للنماذج الأولية المعدنية, use a buffing wheel with polishing compound to achieve a glossy finish. للبلاستيك, يستخدم 800# grit sandpaper followed by isopropyl alcohol to clean the surface.
- المعالجة السطحية: Add spraying (على سبيل المثال, matte black paint for enclosures) أو طباعة شاشة الحرير (على سبيل المثال, logos on phone cases) to mimic the final product.
قائمة مراجعة فحص الجودة
- Dimensional Verification: Use a digital caliper or coordinate measuring machine (CMM) to check key dimensions (على سبيل المثال, قطر الثقب, طول). Ensure errors are within ±0.05mm for most prototypes.
- اختبار وظيفي: Test how the prototype works—e.g., assemble a plastic enclosure with screws to check if parts fit, or bend a metal bracket to test flexibility.
- اختبار المتانة: For industrial prototypes, perform stress tests (على سبيل المثال, drop an ABS enclosure from 1m) to ensure it withstands use.
6. Iteration and Optimization: Improve Based on Feedback
CNC finishing prototypes are not one-time projects—use test results and customer feedback to refine the design or process.
- مثال: A furniture brand tested a CNC finishing prototype of a wooden chair leg (aluminum alloy mockup). Feedback showed the leg was too thin (bent under weight). Engineers adjusted the 3D model to increase thickness from 10mm to 12mm, re-machined the prototype, and passed durability tests.
- Data Recording: Save key data (على سبيل المثال, قصات القطع, material type, inspection results) in a database. This helps speed up future prototype projects—e.g., reusing ABS machining settings for a new enclosure.
Yigu Technology’s Perspective on CNC Finishing Prototype
في Yigu Technology, نعتقد CNC finishing prototype success lies in precision at every step. Many clients struggle with dimensional errors or rough surfaces—our solution is pairing high-precision CNC mills (±0.005mm accuracy) مع نصيحة مواد مصممة. We recommend ABS for low-cost consumer prototypes and aluminum alloy 6061 for industrial parts. Our post-processing team also offers custom spraying and silk screening, قطع النموذج الأولي المهلة 30%. For inspection, we use CMMs to ensure every prototype meets design specs, helping clients launch products faster.
التعليمات
- س: Why is my CNC finishing prototype’s surface rough even after finishing?
أ: Rough surfaces often come from dull tools or high feed rates. Try sharpening the cutting tool or lowering the feed rate by 20% (على سبيل المثال, from 500mm/min to 400mm/min for ABS). أيضًا, check if the machine is calibrated—uncalibrated axes cause uneven cutting.
- س: How long does it take to make a CNC finishing prototype?
أ: ذلك يعتمد على الحجم والمواد. A small ABS enclosure (50x50x30mm) يستغرق 2-3 ساعات (الخشنة + الانتهاء + deburring). A large aluminum bracket (200x150x100mm) takes 5–6 hours. ما بعد المعالجة (تلوين, silk screening) يضيف 1-2 أيام.
- س: Can I use CNC finishing prototypes for mass production testing?
أ: نعم! CNC finishing prototypes are designed to mimic final products, so they’re ideal for testing mass production processes. على سبيل المثال, test if a prototype’s shape fits into injection molds or if its dimensions work with assembly lines—this avoids costly changes later.