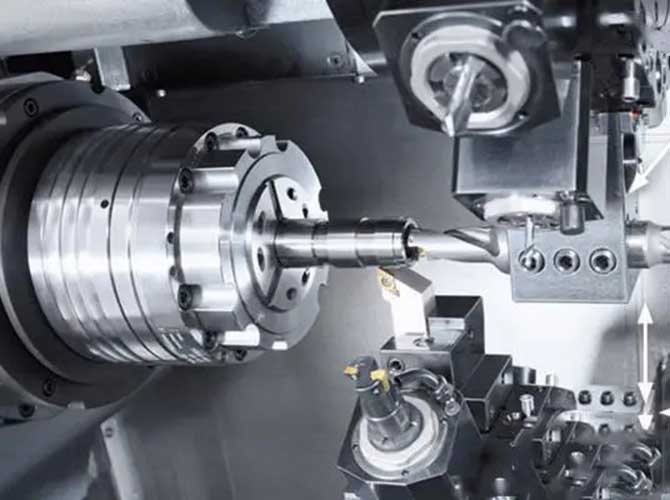
SLM (ذوبان الليزر الانتقائي) is a powerful 3D printing technology for creating high-precision metal parts, but achieving excellent results requires careful attention to every stage of the process. From choosing the right metal powder to post-processing the final part, each step influences the quality, قوة, and reliability of your prints. Let’s explore the essential precautions you need to take when using the SLM process.
اختيار المواد: Choosing the Right Metal Powder
The foundation of successful SLM printing lies in selecting the appropriate metal powder. Since SLM relies on melting metal particles layer by layer, the powder’s properties directly impact the final part’s performance.
- النظر في melting point and physical properties of the metal. Different metals like titanium, الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, and aluminum have varying melting points and mechanical characteristics. على سبيل المثال, titanium alloys offer high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for aerospace parts, while stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for medical or food industry components.
- Pay attention to powder particle size and distribution. Most SLM printers perform best with powder particles ranging from 15 – 45 microns in diameter. A consistent particle size ensures even melting and reduces the risk of defects like porosity. Studies show that using well-graded powder can reduce print defects by up to 30% compared to poorly sorted powder.
Equipment Calibration: Precision Starts Here
Properly calibrated equipment is critical for SLM printing accuracy and consistency.
- Focus on calibrating the laser system regularly. The laser’s power output, focus, and beam alignment must be precise. Even a 0.1mm misalignment can lead to uneven melting and dimensional errors in the final part. Most manufacturers recommend calibrating the laser every 50 – 100 print hours to maintain accuracy.
- Ensure the powder distribution mechanism is working correctly. The system that spreads the powder across the build plate must apply a uniform layer thickness. A variance of more than 5% in layer thickness can cause inconsistencies in part density and strength. Regularly check and clean the recoater blade to prevent powder clumping and uneven spreading.
Parameter Setting: Fine-Tuning for Success
SLM printing involves several critical parameters that need careful adjustment based on the material and part design.
| المعلمة | اعتبارات رئيسية | Typical Range for Stainless Steel |
| Laser Power | Affects melting depth and bond strength; too low causes incomplete melting | 150 – 300 W |
| Scanning Speed | Influences productivity and heat input; faster speeds reduce heat buildup | 800 – 1500 mm/s |
| Layer Thickness | Balances accuracy and speed; thinner layers improve detail but take longer | 20 – 50 ميكرون |
- Match parameters to the material’s properties. على سبيل المثال, materials with higher melting points like titanium may require higher laser power (250 – 400 W) compared to aluminum (100 – 200 W).
- Adjust parameters for part complexity. Intricate designs with thin walls may need slower scanning speeds to ensure complete melting, while larger, simpler parts can use faster speeds to reduce print time.
تصميم هيكل الدعم: Stabilizing Complex Parts
Complex SLM parts with overhangs, ميزات رقيقة, or large unsupported areas require well-designed هياكل الدعم to prevent deformation and ensure print success.
- Place supports strategically under overhangs greater than 45 درجات. These supports act as anchors, reducing warping caused by thermal stress during cooling.
- Design supports with a gradual taper where they connect to the part. This makes post-processing removal easier and minimizes damage to the part’s surface. للأجزاء المعدنية, support structures are often made from the same material as the part to ensure compatible melting and bonding.
ما بعد المعالجة: Enhancing Quality and Performance
Post-processing is essential to transform the as-printed SLM part into a functional, high-quality component.
- Remove unmelted powder كاملاً. Use compressed air or vacuum systems to clean powder from internal channels and surface crevices. Residual powder can cause issues in final use, especially for moving parts or components exposed to high temperatures.
- يعتبر المعالجة الحرارية to relieve internal stresses. SLM parts often have residual stresses from the rapid heating and cooling cycles. Annealing or stress-relief heat treatment can improve the part’s mechanical properties, increasing ductility by up to 20% in some cases.
- Sanding and finishing improve surface quality. As-printed SLM parts may have a rough surface with layer lines. Sanding with 200 – 800 grit sandpaper or using abrasive blasting can achieve a smooth finish, which is important for parts that need to meet tight tolerance requirements or have aesthetic needs.
Safe Operation: Protecting Yourself and Equipment
SLM printing involves high temperatures and laser exposure, making safety protocols a top priority.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes heat-resistant gloves to prevent burns, laser safety glasses to protect eyes from harmful radiation, and a respirator to avoid inhaling metal powder particles.
- Follow laser safety guidelines strictly. Never look directly at the laser beam, and ensure the printer’s enclosure is properly closed during operation. Laser injuries can cause permanent eye damage, so adherence to safety rules is non-negotiable.
- Handle metal powder safely. Store powder in sealed containers to prevent contamination and avoid creating dust clouds, which can be a fire hazard. Clean up spills immediately using approved methods to prevent slips and inhalation risks.
فعالية التكلفة: Balancing Quality and Budget
While SLM offers exceptional precision, it’s important to consider cost factors to ensure the process is economically viable for your project.
- Evaluate material usage. SLM can produce parts with complex geometries that minimize material waste compared to traditional machining, but metal powder is still expensive. Optimize your part design to use only necessary material, reducing powder consumption by 10 – 30% in some cases.
- Plan for equipment and maintenance costs. SLM printers have higher upfront costs than some other 3D printing technologies, and regular maintenance (like laser replacement and system cleaning) adds to the expense. Factor these costs into your project budget and consider batch printing similar parts to maximize machine utilization.
ضبط الجودة: Ensuring Consistency Layer by Layer
Implementing strict quality control measures throughout the printing process helps catch issues early and ensures part reliability.
- Monitor layer adhesion and density regularly. Use in-process monitoring tools if available, or pause the print periodically to inspect a cross-section of layers. Look for signs of incomplete melting, porosity, or cracks, which can indicate parameter issues.
- Perform dimensional checks after printing. Use coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or 3D scanners to verify that the part meets design specifications. Tolerances as tight as ±0.05mm are achievable with SLM, but only with proper quality control.
- Test mechanical properties for critical parts. Conduct tensile tests, hardness tests, or impact tests on sample parts to ensure they meet the required strength and performance standards. This is especially important for parts used in safety-critical applications like medical implants or aerospace components.
Environmental Control: Keeping Powder Dry and Clean
Metal powder is highly susceptible to moisture, which can negatively affect print quality.
- Maintain a dry environment for powder storage and printing. The ideal relative humidity for SLM operations is below 30%. Use dehumidifiers in the printing area and store powder in moisture-controlled containers. Moisture in powder can cause gas porosity in the printed part, weakening its structure.
- Prevent contamination of the powder. Keep the printing chamber and powder handling areas clean to avoid mixing different powder types or introducing debris. Even small amounts of contamination can lead to defects in the final part, compromising its performance.
تنسيق الملف والتقطيع: Preparing Files for Success
Proper file preparation ensures your design translates accurately into a printed part.
- يستخدم compatible file formats for your SLM printer. STL and 3MF formats are widely supported, but check your printer’s specifications for recommended formats. Ensure the 3D model is watertight with no missing faces, as these errors can cause slicing issues.
- Optimize slicing settings for SLM. Adjust parameters like hatch spacing (distance between laser scan lines) and scan pattern to balance build speed and part density. A smaller hatch spacing (0.1 – 0.2مم) increases density but reduces speed, while a larger spacing does the opposite. Always preview the sliced model to identify potential issues before printing starts.
مراقبة عملية الطباعة: اصطياد القضايا في وقت مبكر
Vigilant monitoring during printing can prevent costly failures and wasted materials.
- Watch the first few layers closely. This is when many issues like poor bed adhesion or uneven powder spreading become apparent. If you notice the first layer isn’t adhering properly, stop the print, clean the build plate, and adjust the laser power or bed temperature.
- Keep an eye on laser positioning and powder distribution. Misaligned lasers or clogged recoater blades can cause uneven melting or layer shifts. Most modern SLM printers have sensors that alert operators to these issues, but manual checks are still valuable.
- Note any unusual sounds or smells. Strange noises may indicate mechanical problems with the printer, while burning smells could signal excessive heat or powder contamination. Address these issues immediately to prevent damage to the printer or part.
الاختبار والمعايرة: Validating Settings Before Full Production
Before starting a large batch of prints, small-scale test prints are essential to validate your setup.
- Print a test coupon with features representative of your final part, such as thin walls, overhangs, and holes. This allows you to check for dimensional accuracy, الانتهاء من السطح, and internal quality without wasting large amounts of powder.
- Use test results to fine-tune parameters. If the test part has porosity, increase laser power or decrease scanning speed. If dimensions are off, recalibrate the laser alignment or adjust slicing settings. Once the test print meets your standards, you can proceed with confidence to full production runs.
Yigu Technology’s View
SLM 3D printing demands meticulous attention to material, حدود, and safety for high-quality metal parts. From precise calibration to strict quality control, each step impacts performance. في Yigu Technology, we emphasize these precautions to ensure print reliability, فعالية التكلفة, and meet diverse industrial needs, leveraging SLM’s potential for complex, high-performance components.
التعليمات
- What particle size is best for SLM metal powder?
Most SLM printers perform optimally with metal powder particles ranging from 15 – 45 microns in diameter, ensuring even melting and reducing defects.
- How often should SLM equipment be calibrated?
The laser system should be calibrated every 50 – 100 print hours, and the powder distribution mechanism checked regularly to maintain layer thickness consistency.
- Why is post-processing important for SLM parts?
Post-processing removes residual powder, relieves internal stresses through heat treatment, and improves surface finish, enhancing the part’s mechanical properties and functionality.